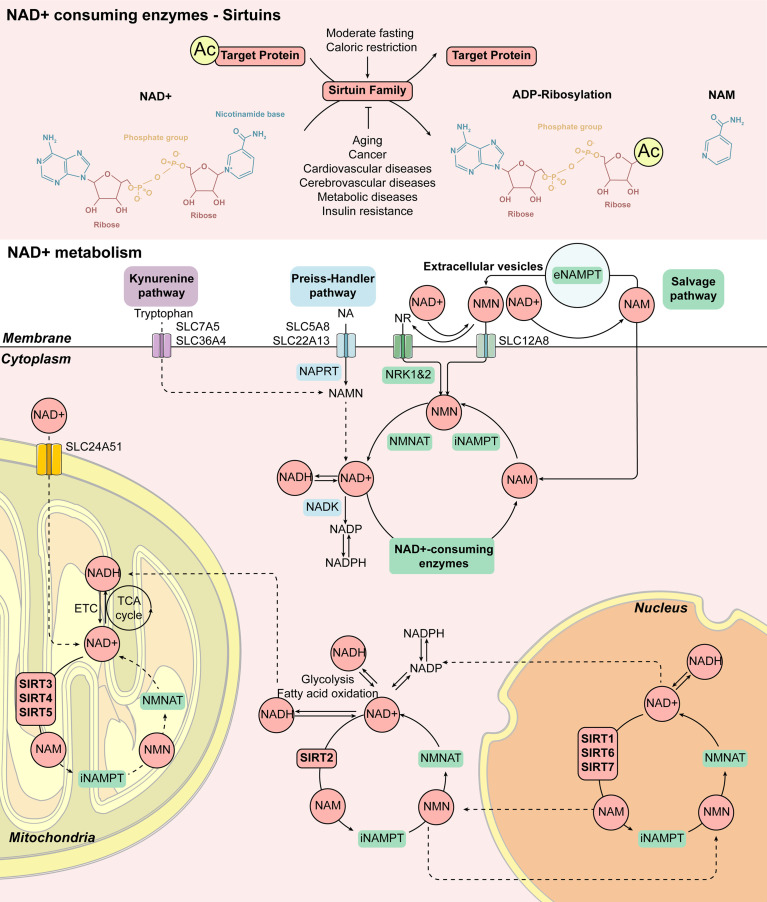
Figure 2.
Cellular NAD+ metabolism induced by Sirtuin family. The enzymatic activity of the Sirtuin family is mainly to remove the acetyl group from the target protein. Firstly, NAD+ is cut into NAM and ADP-ribose, and the acetyl group on the target protein is transferred to ADP-ribose to form acetyl-ADP-ribose. Therefore, some members of the Sirtuin family can also play a role in ADP ribosyltransferase. The increase of NAD+ levels is closely related to the activation of the Sirtuin family members during moderate fasting and caloric restriction. On the contrary, aging, cancer, cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases as well as metabolic diseases such as insulin resistance lead to a decrease in NAD+ levels, which is related to the decrease in Sirtuin family activity. Mammalian cells can produce NAD+ from Tryptophan via the Kynurenine pathway or from NA, one of the forms of vitamin B3, via the Preiss-Handler pathway, while most NAD+ is recovered from NAM and NR via the Salvage pathway. NAD+ can be reduced to NADH during glycolysis, fatty acid oxidation, and the TCA cycle. NAD+ also acts as a substrate for enzymes such as Sirtuins, producing NAM as a byproduct, and affects metabolism, genomic stability, gene expression, inflammation, circadian rhythm, and stress resistance. This response pattern of the Sirtuin family is extensive. SIRT1, SIRT6, and SIRT7 exist in the nucleus, SIRT2 exists in the cytoplasm, while SIRT3, SIRT4, and SIRT5 exist in the mitochondrion. Abbreviations: Ac, acetylation; eNAMPT, extracellular nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase; ETC, electron transport chain; iNAMPT, intracellular nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase; MNAM, N 1-methylnicotinamide; NA, nicotinic acid; NAD+, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; NADH, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; NADK, NAD+ kinase; NADP/NADPH, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; NAM, nicotinamide; NAMN, nicotinamide mononucleotide; NAPRT, nicotinic acid phosphoribosyltransferase; NMN, nicotinamide mononucleotide; NMNAT, nicotinamide mononucleotide adenylyltransferases; NR, nicotinamide riboside; NRK1&2, nicotinamide riboside kinases 1 and 2; TCA, tricarboxylic acid.