Figure 1. Representation in the 12 eligible US or Canadian acute ischemic stroke trials published between 2010 and 2020.
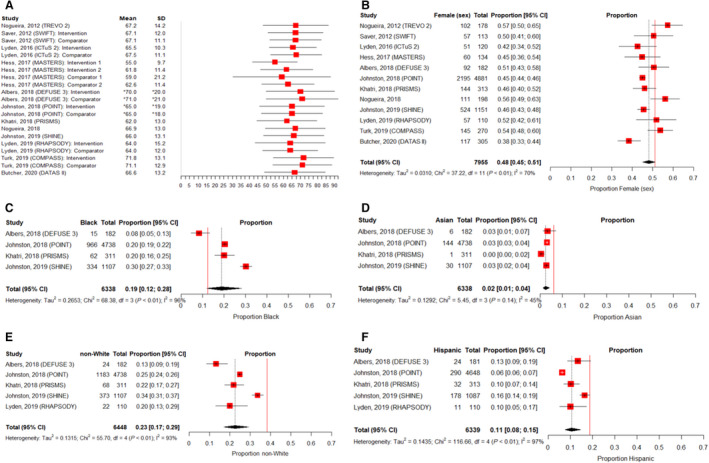
A, Measures of central tendency and distribution for age by trial/trial intervention group.† B, Pooled proportion of female (sex) participants (pooled proportion of acute ischemic stroke RCT participants=48%; proportion of the general US population=51%).‡ C, Pooled proportion of Black participants (pooled proportion of acute ischemic stroke RCT participants=19%; proportion of the general US population=12.4%).‡ D, Pooled proportion of Asian participants (pooled proportion of acute ischemic stroke RCT participants=2%; proportion of the general US population=6%).‡ E, Pooled proportion of non‐White participants (pooled proportion of acute ischemic stroke RCT participants=23%; proportion of the general US population=38.4%).‡ F, Pooled proportion of Hispanic participants (pooled proportion of acute ischemic stroke RCT participants=11%; proportion of the general US population=18.7%)‡. *In accordance with the format of age reporting in the RCT publications, age median and interquartile range were presented in place of mean and SD. †Error bars=mean +/− 1.35 SDs or median +/− 1 interquartile range. ‡To provide a visual comparator, the vertical, solid red line indicates the approximate proportion of each of the assessed groups within the general US population based on 2019 and 2020 census data. 6 , 7 RCT indicates randomized controlled trial.
