Figure 2. Tornado diagram for the 1‐way deterministic sensitivity analyses.
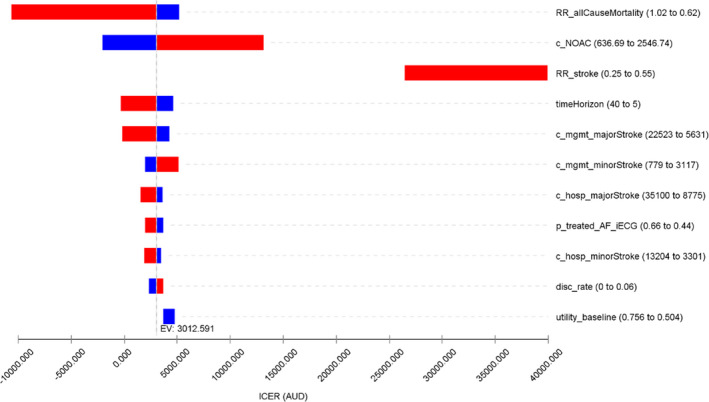
Incremental net monetary benefit was calculated according to the willingness‐to‐pay/quality‐adjusted life‐year threshold of $50 000. The expected value at base case suggests that smartphone‐based handheld ECG device (iECG) is associated with an incremental cost‐effectiveness ratio of $3013/quality‐adjusted life‐year in the base case scenario. RR_stroke and utility_baseline do not align with the base case line as they both impact the results of iECG and standard care arms. c_NOAC indicates cost of new oral anticoagulant medications; c_hosp_majorStroke, cost of hospitalization for a major stroke; c_hosp_minorStroke: cost of hospitalization for a minor stroke; c_mgmt_majorStroke, annual management cost post a major stroke; c_mgmt_minorStroke, annual cost of management post a minor stroke; disc_rate, discount rate; EV, expected value; ICER, incremental cost‐effectiveness ratio; p_treated_AF_iECG, probability of initiating oral anticoagulant treatment after AF detection by iECG; RR_allCauseMortality, relative risk of all cause mortality for oral anticoagulant treated vs non‐oral anticoagulant treated patients; RR_stroke, relative risk of stroke for oral anticoagulant treated vs non‐oral anticoagulant treated patients; timeHorizon, long‐term modeled time horizon; and utility_baseline, utility weight for being post an ischemic stroke at baseline.
