Figure 4. Impact of the RhoA (Ras homolog gene family, member A)/ROCK (rho associated coiled‐coil containing protein kinase) pathway on VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor)‐induced angiogenic endothelial cell sprouting and basal migration.
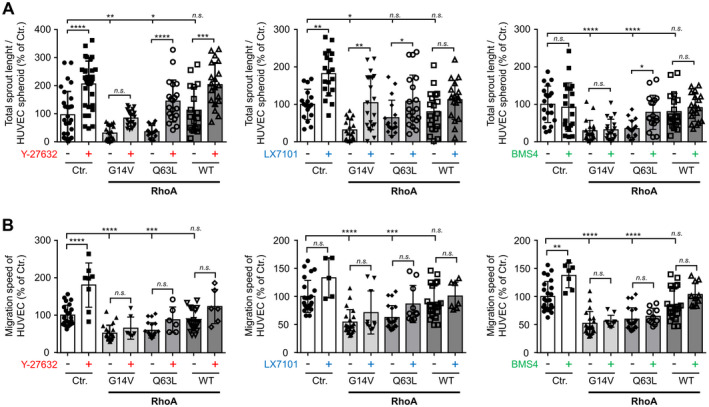
A, VEGF‐stimulated (20 ng/mL) human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) spheroid‐based sprouting assay using control‐transduced (Ctr.) HUVEC or HUVEC expressing constitutively active RhoA (G14V, Q63L) or RhoA wild‐type (WT) in the presence (+) or absence (−) of the ROCK inhibitor Y‐27632 (10 µmol/L), the LIMK2 (LIM domain kinase 2) inhibitor LX7101 (3 µmol/L), or the LIMK1 (LIM domain kinase 1) inhibitor BMS4 (0.5 µmol/L), respectively. Statistical analysis of total sprout length. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001 vs control‐transduced HUVEC (n=16–34). B, Statistical analysis of migration speed of HUVEC expressing different RhoA variants and kept in presence (+) or absence (−) of the ROCK inhibitor Y‐27632 (10 µmol/L), the LIMK2 inhibitor LX7101 (3 µmol/L), or the LIMK1 inhibitor BMS4 (0.5 µmol/L). ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001 vs control‐transduced HUVEC (n=5–24). n.s. indicates not significant.
