Figure 5. p53CKO animals fail to develop HEpEF upon HFD+L‐NAME challenge.
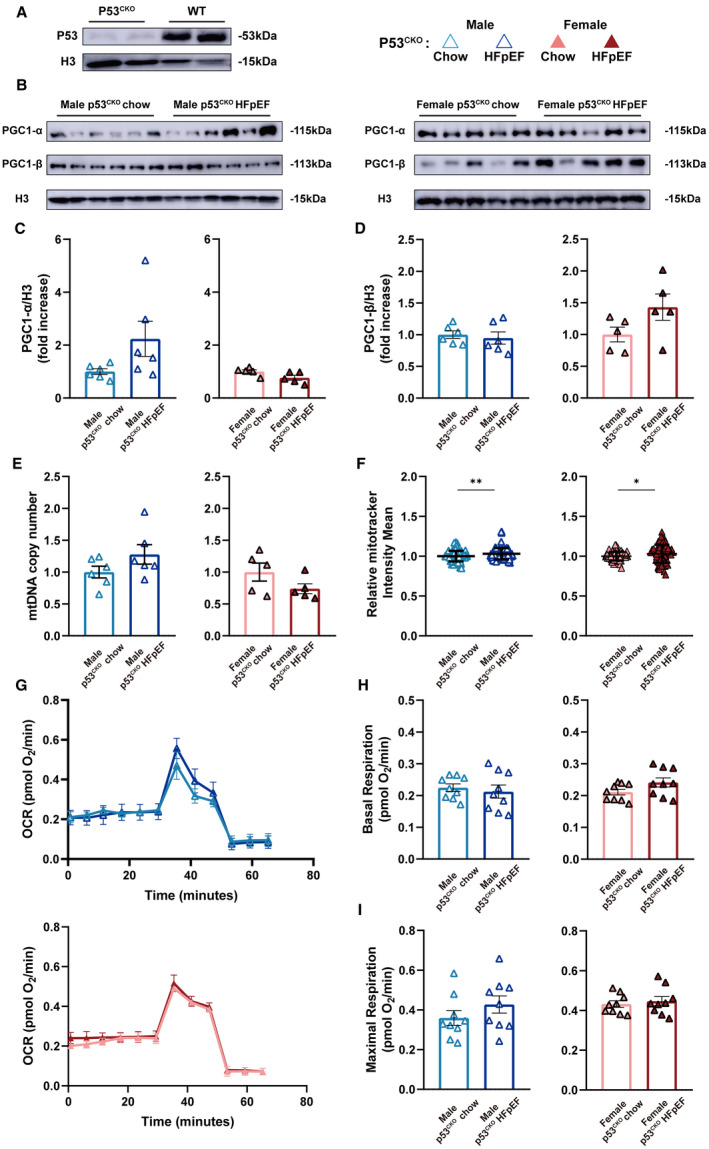
A and B, Representative immunoblots of p53, Pgc1‐α, and Pgc1‐β expression in isolated AMVMs are shown. Histone H3 used as loading control. C and D, Densitometric quantifications of Pgc1‐α and Pgc1‐β expression. Results are shown as mean±SEM (n=6 per male p53CKO group; n=5 per female p53CKO group). E, mtDNA copy number in AMVMs was determined by real‐time quantitative polymerase chain reaction and is shown as mean±SEM (n=6 per male p53CKO group; n=5 per female p53CKO group). F, Mitochondrial amount was assayed using Mitotracker staining and is shown as mean±SD (n=6 per male p53CKO group; n=5 per female p53CKO group; 15 AMVMs per mouse). G, Real‐time mitochondrial respiration of AMVMs (n=3 per group). H and I, Basal and maximal OCR of AMVMs were quantified and are shown as mean±SEM (n=3 per group; 3 measurements per mouse). Mann‐Whitney test was used for panel F; 2‐tailed unpaired Student's t test was used for remaining analyses. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 compared with chow group. AMVM indicates adult mouse ventricular cardiomyocyte; HFD, high‐fat diet; HFpEF, heart failure with preserved ejection fraction; L‐NAME, Nω‐Nitro‐L‐arginine methyl ester hydrochloride; OCR, oxygen consumption rate; p53CKO, cardiomyocyte‐specific p53 knockout; PGC1‐α, proliferator‐activated receptor gamma, coactivator 1 alpha; and PGC1‐β, proliferator‐activated receptor gamma, coactivator 1 beta.
