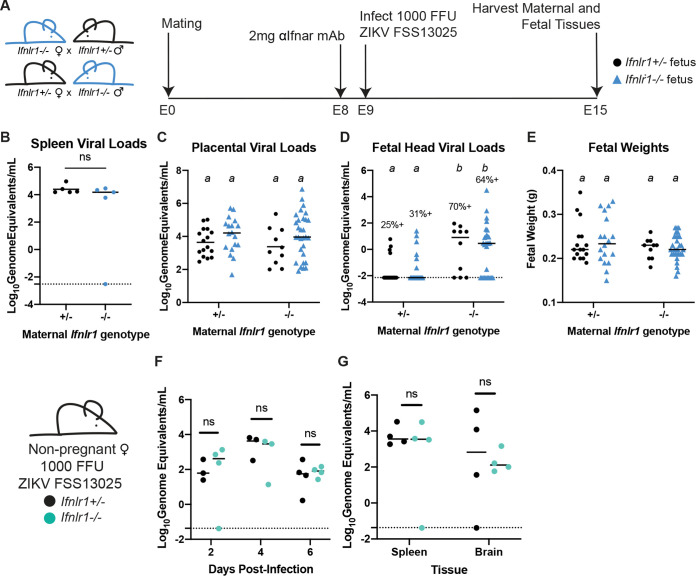
FIG 3.
IFN-λ restricts ZIKV transplacental transmission by signaling to maternal tissues. (A) Mating and infection timeline. Ifnlr1+/− dam × Ifnlr1−/− sire and Ifnlr1−/− dam × Ifnlr1+/− sire crosses were used to generate pregnancies with IFN-λ responsive (Ifnlr1+/−) and nonresponsive (Ifnlr1−/−) fetuses. (B to E) Pregnant dams were treated with 2 mg of IFNAR1 blocking antibody at E8 and infected at E9 with 1,000 FFU of ZIKV FSS13025 by subcutaneous inoculation in the footpad. Fetuses and their associated placentas were harvested at E15. ZIKV RNA was measured by qRT-PCR in maternal spleen (B), placenta (C), and fetal head (D), and fetuses were weighed (E). (D) The percent of fetuses with detectable ZIKV is noted. Data are combined from 5 or 6 dams per group; each data point represents a single dam (B) or fetus (C to E). Groups were compared by ANOVA (B, C, E) or Mann-Whitney (D); italicized letters indicate groups that are significantly different from each other (P < 0.05). (F and G) Nonpregnant, 8-week-old Ifnlr1−/− and Ifnlr1+/− females were infected with 1,000 FFU of ZIKV FSS13025. Viremia was measured from serum at 2, 4, and 6 dpi by qRT-PCR. Spleens and brains were harvested 6 dpi, and viral loads were measured by qRT-PCR. Groups were not significantly different (ns) by ANOVA.