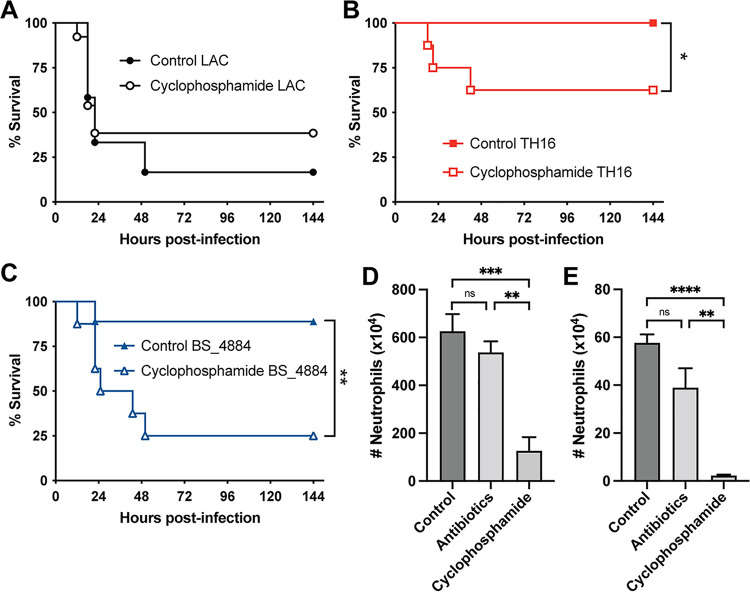
FIG 8.
Antibiotics in drinking water increased susceptibility to infection without ablating neutrophils. (A to C) C57BL/6J mice were treated with cyclophosphamide intraperitoneally for 1 week and subsequently infected intranasally with LAC (A), TH16 (B), and BS_4884 (C), and survival was measured (n = 8 to 13 mice/group). (D and E) The numbers of neutrophils in the bone marrow (D) and the spleen (E) were quantified using flow cytometry (n = 4 to 5 mice/group) (means ± SEM). Statistical analysis was performed using a log rank (Mantel-Cox) test (A to C) and two-way ANOVA with a Šídák posttest (D and E). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.005; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001; ns, not significant.