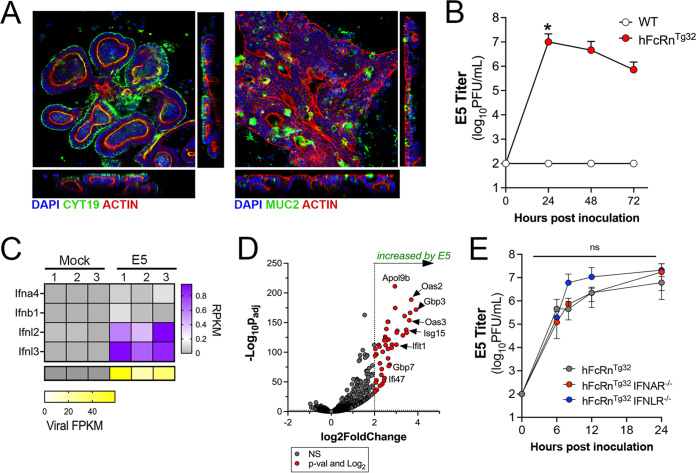
FIG 1.
Human FcRn is necessary and sufficient for echovirus infection of murine-derived primary enteroids. (A) Murine enteroids were generated from Lgr5+ crypts isolated from the small intestines of five 10-day-old neonatal C57BL/6J (WT) mice. Confocal microscopy images of enteroids immunostained with cytokeratin-19 in green and actin in red (left) or mucin-2 in green and actin in red (right) ~10 days after culturing are shown. (B) WT (white) or hFcRnTg32 (red) enteroids were generated from small intestine tissue from 10-day-old neonatal mice and infected with 106 PFU of neutral red-incorporated E5. Viral titers (log10 PFU per milliliter) were assessed in the cell culture supernatants at the indicated time points. (C) Heatmap of reads per kilobase per million (RPKM) values of the type I IFNs Ifna4 and Ifnb1 and the type III IFNs Ifnl2 and Ifnl3 from bulk RNASeq of uninfected (mock) or E5-infected hFcRnTg32 enteroids at 24 h postinfection. In the key at the right, purple indicates higher reads, and gray denotes no reads detected. At the bottom are viral fragments per kilobase per million (FPKM) values from the samples shown at the top. Yellow indicates high viral RNA reads, and gray denotes no reads detected. (D) Volcano plot comparing differentially expressed transcripts in E5-infected hFcRnTg32 enteroids compared to mock controls as determined by DESeq2 analysis. Gray circles represent genes whose expression was not significantly changed (NS). Red circles represent genes that were significantly changed by E5 infection. Significance was set at a P value of <0.01 and a log2 fold change of ±2. (E) Enteroids generated from the small intestine of hFcRnTg32 (gray), hFcRnTg32-IFNAR−/− (red), or hFcRnTg32-IFNLR−/− (blue) mice were infected with 106 PFU of neutral red-incorporated E5. Viral titers (log10 PFU per milliliter) are shown at the indicated time points. In panels B and E, data are shown as means ± standard deviations from three independent replicates. Enteroids were isolated from at least five 10-day-old neonatal mice and pooled during Lgr5+ crypt isolation. Significance in panel B was determined by a Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s test for multiple comparisons. Significance in panel D was determined using two-way ANOVA with a Geisser-Greenhouse correction and Tukey’s multiple-comparison test (*, P < 0.05; ns, not significant).