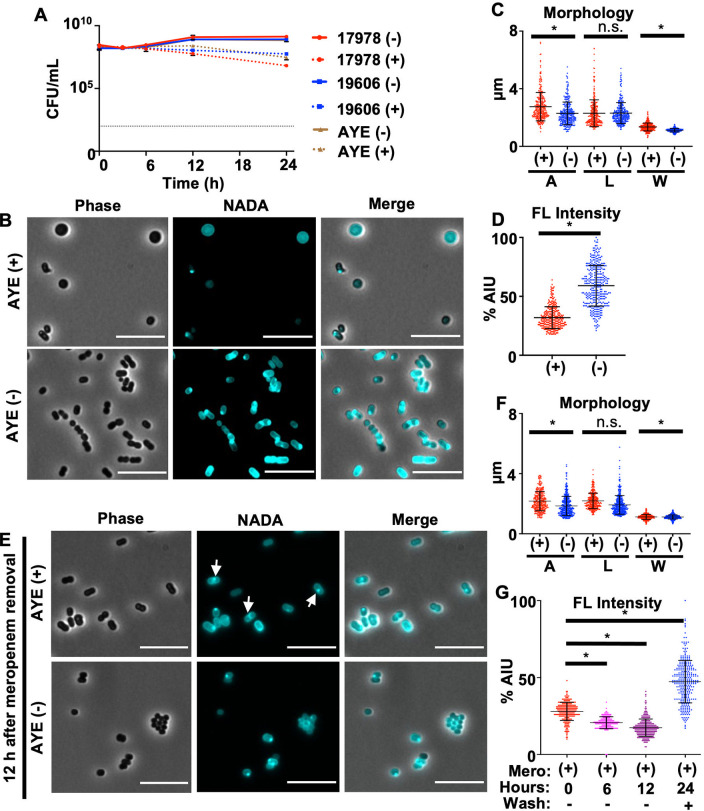
FIG 1.
Acinetobacter baumannii strains are tolerant to meropenem. (A) CFU of A. baumannii strains ATCC 17978, ATCC 19606, and AYE untreated (−) or treated (+) with meropenem over 24 h. Each killing assay was independently replicated three times, and one representative data set is reported. Error bars indicate standard deviations (SD) from the means. The dotted black line indicates the level of detection. (B) Phase-contrast and fluorescence microscopy of treated or untreated A. baumannii strain AYE after 12 h. Bars, 10 μm. (C) Area (A), length (L), and width (W) quantitations of cells in panel B (n = 300). (D) Fluorescence (FL) signal intensity quantitation in percent arbitrary intensity units (AIU) of treated versus untreated cells in panel B (n = 300). (E) After 12 h of meropenem treatment, the antibiotic was removed, and cells were resuspended in fresh medium without the antibiotic and stained with NADA. Cells were imaged after a 12-h recovery period and showed that the characteristic coccobacillus morphology was restored. White arrows indicate fluorescence intensity at the midcell. (F) Area, length, and width (W) of cells in panel E (n = 300). (G) Fluorescence signal intensity in percent AIU for treated versus untreated cells (n = 300) at 0, 6, and 12 h during meropenem treatment and 12 h after the removal of the antibiotic. Significance was determined using an unpaired t test (P < 0.05) in treated versus untreated cells. An asterisk indicates significant differences between treated and untreated cells. n.s., not significant. Error bars indicate SD from the means.