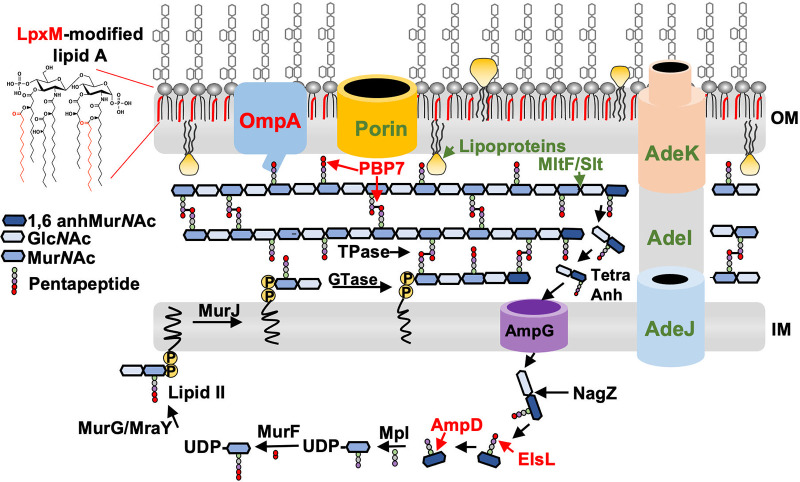
FIG 6.
Model showing mechanisms that promote meropenem tolerance in A. baumannii. Based on transcriptomic analysis, several genes are differentially expressed after treatment with high levels of meropenem. Pathways include the upregulation of the AdeIJK efflux pump, lipoproteins, and the MltF/Slt autolysins, while porins, including CarO and OprD, were downregulated (green). Fitness screens showed that several genes involved in the outer membrane (OM), periplasmic, and cytoplasmic pathways promote meropenem tolerance. Pathways include OmpA, which tethers the outer membrane to the peptidoglycan; LpxM, which increases hydrophobic packing in the outer membrane; the dd-carboxypeptidase and dd-endopeptidase PBP7; and the cytoplasmic recycling enzymes ElsL and AmpD (red). Autolysin activity is shown at the 1,6-anhMurNAc end of the glycan chain, but it is not known from which ends MltF/Slt release the muropeptide. It is also possible that ElsL could act before NagZ. IM, inner membrane; Tpases, transpeptidase; GTase, glycosyltransferase.