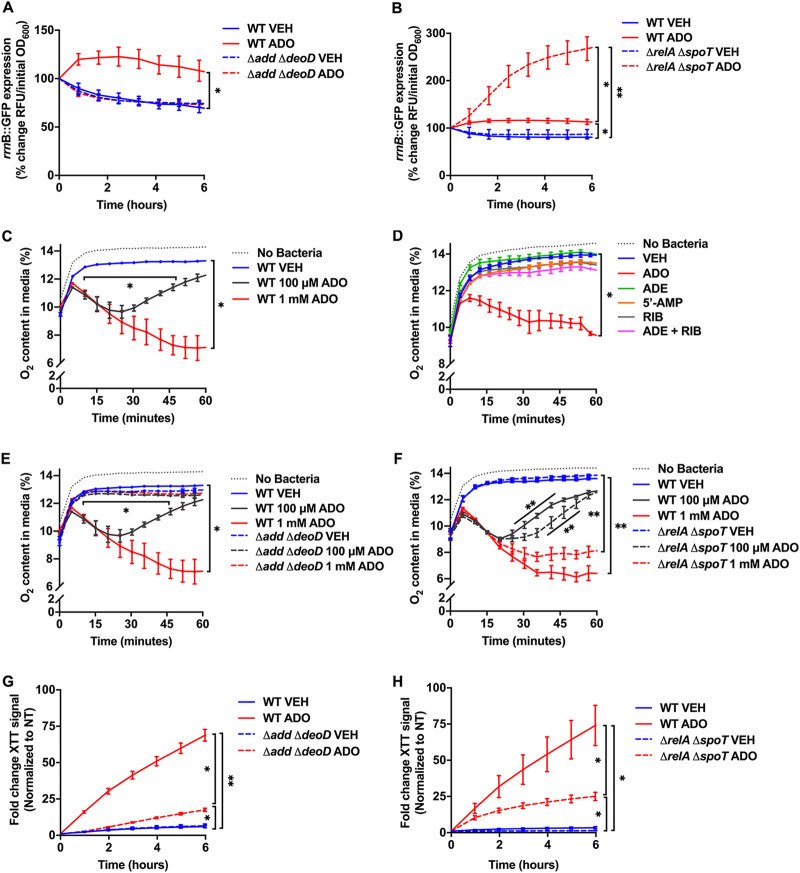
FIG 2.
ADO hyperstimulates rRNA transcription, O2 respiration, and electron transport chain activity. (A and B) rrnB P1:GFP signal from wild-type and mutant E. coli following the downshift from LB broth to PBS. Selected samples were treated with 1 mM ADO at time zero. Fluorescent signal and OD600 were monitored over time at 37°C. Signal was normalized to initial inoculum. (C to F) O2 consumption was examined in PBS with E. coli at 37°C in a shaker incubator using PreSens OxoDish. Dotted gray line indicates O2 content in cell-free media. (G and H) Tetrazolium dye, XTT, in PBS; for each time point, the signal was normalized to the time zero of the wild-type vehicle control group. Readings were taken every 10 min at 37°C. No growth was observed under experimental conditions in panels A to H. Data are the mean of three biological replicates ± SEM. *P, < 0.05; **, P < 0.01, as estimated by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison. ADE, adenine; ADO, adenosine; RIB, d-ribose; RFU, relative fluorescent unit; VEH, vehicle control.