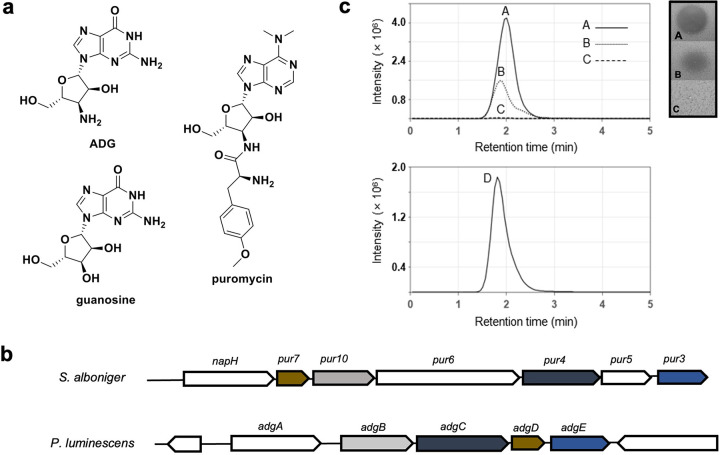
FIG 1.
ADG structure and biosynthetic gene cluster (BGC). (a) Structures of ADG, guanosine, and puromycin. (b) Comparison between the puromycin BGC from S. alboniger and the ADG BGC from P. luminescens. The color-coded genes highlighted are homologs between the two BGCs. (c) Heterologous expression of ADG. Extracted ion chromatogram (EIC; m/z 283.11 to 283.19) on the left and inhibitory activity on E. coli lawn on the right of ADG standard (60 ng/mL ADG in H2O) (line A), partially purified extract of E. coli Bap1+pNS-ADG (line B), partially purified extract of E. coli Bap1+pRSFduett-1 (negative control) (line C), and EIC (m/z 283.11 to 283.19) of coinjection of lines A and B (line D).