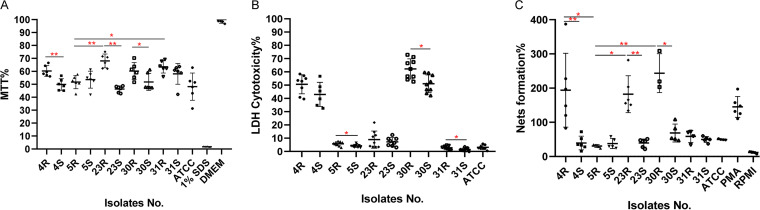
FIG 10.
Cytotoxicity of A. actinomycetemcomitans in different human cell infection models. (A) The viability of A253 epithelial cells infected with A. actinomycetemcomitans R isolates or S strains (MOI = 100) was assessed by determining MTT reduction at 6 h postinfection. For a control, the cells were either killed with 1% SDS or supplemented with fresh DMEM. (B and C) Human neutrophils were infected with A. actinomycetemcomitans (MOI = 100), and at 2 h postinfection, neutrophil lysis was evaluated by measuring the release of LDH (B) and NET formation was evaluated by measuring DNA release by high-throughput microscopy (C). For the assessment of NETosis in panel C, NETosis was induced with 0.125 μg/mL (20 nM) PMA. Fresh RPMI medium was added as a negative control. Statistically significant differences were assessed with Kruskal-Wallis tests with subsequent Dunn’s or Dunnett’s multiple-comparison tests (*, P < 0.03; **, P < 0.002).