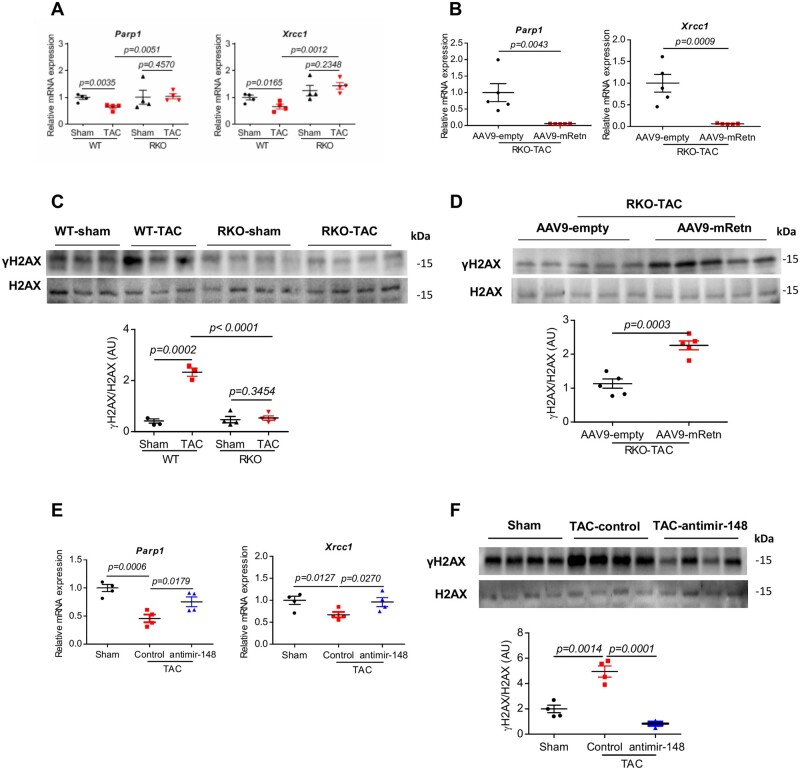
Figure 5.
Effect of Retn and inhibition of miR148b-3p on DNA damage and DDR after TAC-induced mice HF. (A) Real-time PCR analysis of the expression levels of DNA repair-related genes (Parp1 and Xrcc1) in WT and RKO mice subjected to sham or TAC for 10 weeks (n = 4). (B) Real-time PCR analysis of the expression levels of Parp1 and Xrcc1 in AAV9-empty or AAV9-mRetn RKO mice subjected to TAC for 7 weeks (n = 5). (C) Western blot and quantification heart expression of γH2AX in WT and RKO mice subjected to sham or TAC for 10 weeks (n = 3–4). (D) Western blot and quantification heart expression of γH2AX in AAV9-mRetn vs. AAV9-empty controls (n = 5). (E) Real-time PCR analysis of the expression levels of Parp1 and Xrcc1 in sham and TAC-induced WT mice ± anti-miR-148b-3p (n = 4). (F) Western blot and quantification heart expression of γH2AX in sham and TAC-induced WT mice ± anti-miR-148b-3p (n = 4). Protein levels were normalized to GAPDH, a loading control; mRNA levels were normalized to 18S. N, each animal is shown as an individual point whereas horizontal lines represent median values. Values are shown as mean± S.E.M. with each experiment performed in biological and technical replicates as indicated. Significance was evaluated by Student’s t-test or one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test. P values <0.05 were considered significant.