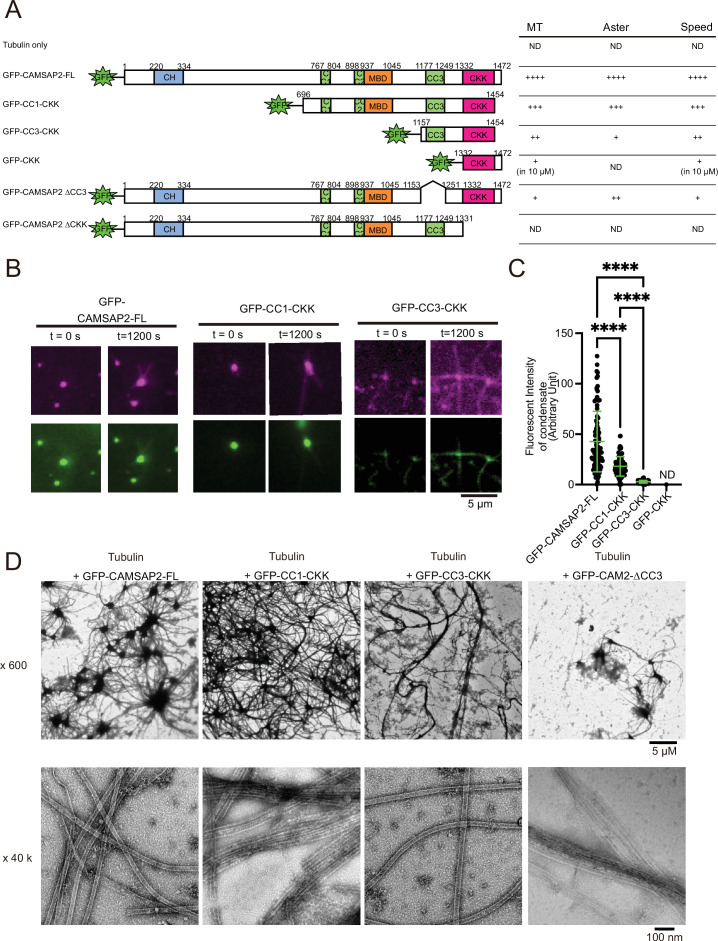
Figure 6. Functional domain mapping of the microtubule nucleation and aster formation activity of calmodulin-regulated spectrin-associated protein 2 (CAMSAP2).
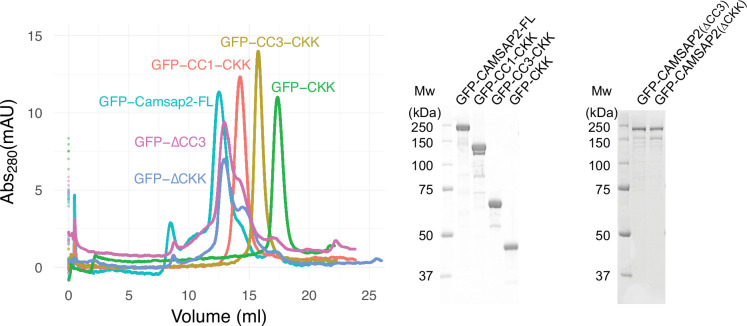
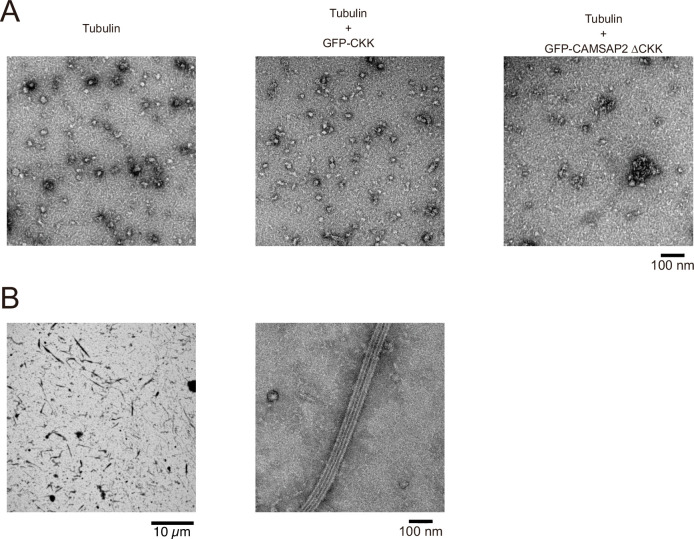
(A) Microtubule nucleation and aster formation activities of CAMSAP2 deletion constructs evaluated by the results of 10 µM tubulin with 1 µM CAMSAP2. The number of ‘+’ symbols indicates the strength of the activity (++++, strongest; +, weakest; ND, not detected). Size exclusion chromatography and SDS-PAGE of GFP fused constructs are available in Figure 6—figure supplement 1. CH, calponin-homology domain; MBD, microtubule-binding domain; CC, coiled-coil domain; CKK, C-terminal domain common to CAMSAP1 and two other mammalian proteins, KIAA1078 and KIAA1543. (B) Microtubule growth from CAMSAP2 condensates composed of full-length and deletion constructs. In vitro reconstitution was performed as described in Figure 4I. (C) Fluorescent intensity of CAMSAP2 condensates at 0 s. ND means that the fluorescent intensity of condensates could not be measured because GFP-CKK did not induce any condensates. Ordinary one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. ****, p<0.0001. n=100 condensates from three independent preparations. (D) Negative stain EM images of polymerization by 10 µM tubulin with 1 µM GFP-CAMSAP2-FL or 1 µM CAMSAP2 mutants during 10 min of incubation at 37°C. The results for tubulin alone and GFP-CKK are available in Figure 6—figure supplement 3. Representative EM images are shown from at least three independent assays.