Figure 2. γCaMKII is enriched in GABAergic interneurons in the mouse hippocampus and cortex.
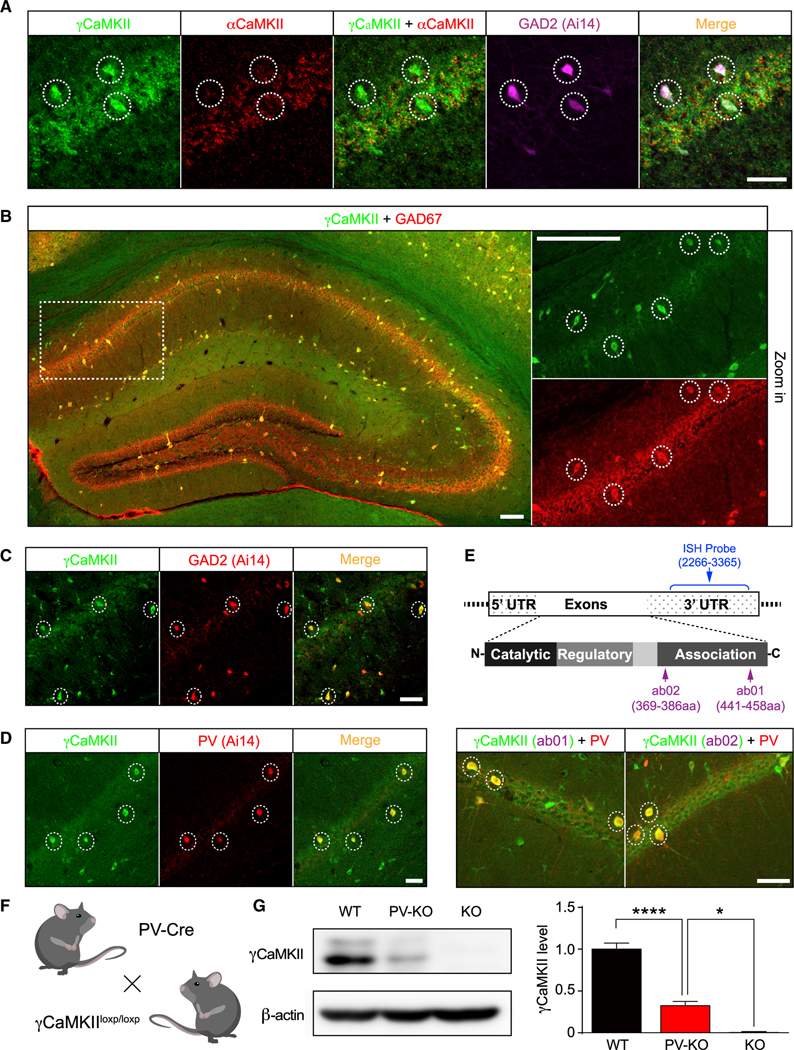
(A) γCaMKII mRNA levels are high in αCaMKII-negative/GAD2-positive neurons (dashed circles) in the hippocampus.
(B) γCaMKII protein levels are high in GAD67+ interneurons (dashed circles) in the hippocampus.
(C and D) Hippocampal sections obtained from GAD2::Ai14 (tdT) and PV::Ai14 (tdT) mice reveal high γCaMKII expression in GAD2+ and PV+ interneurons (dashed circles).
(E) Top, schematic illustration of the γCaMKII mRNA and proteins, showing the regions recognized by the ISH probe (nucleotides 2266–3365) and the antibodies ab01 (amino acids 441–458) and ab02 (amino acids 369–386). Bottom, representative images showing γCaMKII ab01 (left) and ab02 (right) immunostaining in PV+ interneurons (dashed circles) in the hippocampus. For (A)–(E), see Figures S1 and S3 for the distribution in the cortex.
(F) γCaMKII PV-KO mice were generated by crossing γCaMKIILoxP/LoxP mice with PV-Cre mice.
(G) Example western blot analysis and summary of γCaMKII in the hippocampus of wild-type (WT), PV-KO, and KO mice (n = 4–7 mice/group).
In this and subsequent figures, summary data are presented as the mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05 and ****p < 0.0001 (one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test). Scale bar: 50 μm (A and C–E) and 100 μm (B). See also Figures S1–S3.
