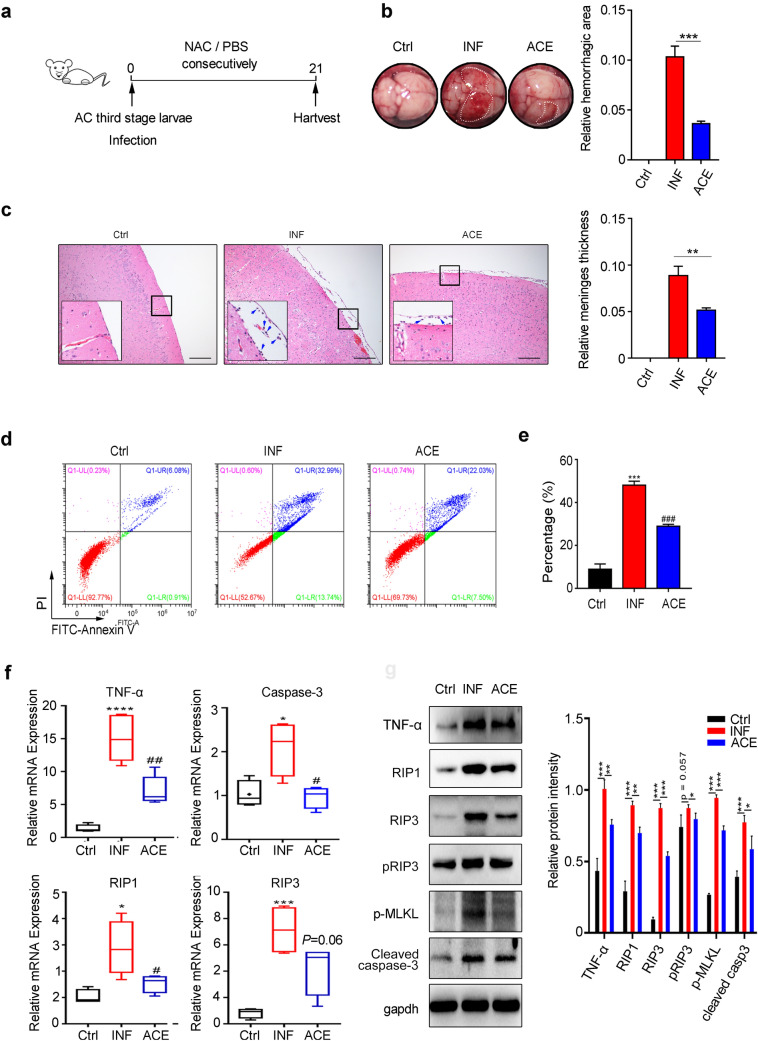
Fig. 3.
Inhibition of TNF-α alleviates the inflammation and cell death of mouse brains with AC infections. a Mice (n = 4 per group) were consecutively administered ACE or PBS after AC infection. b Representative images of brain tissues in mice from three groups (left) and quantitative analysis for relative haemorrhagic surface area (right). c Pathological morphology of brain tissues was evaluated by H&E staining (left) and quantitative analysis for relative meninges thickness in H&E staining (right). d Flow cytometry analysis was used to analyse the cell death of mouse brains. e Percentage of dead cells showed in d. f mRNA levels of TNF-α, RIP1, RIP3 and Caspase-3 were detected after ACE treatment (n = 4 mice/group). g Protein levels of RIP1, RIP3, pRIP3, pMLKL and cleaved caspase-3 in mouse brains of the three groups were examined by western blot (left) and quantitative analysis for protein intensity (right, normalized to GAPDH). ACE acetylcysteine. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001. ****p < 0.0001 compared to the Ctrl group, #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01 compared to the INF group (student’s t test)