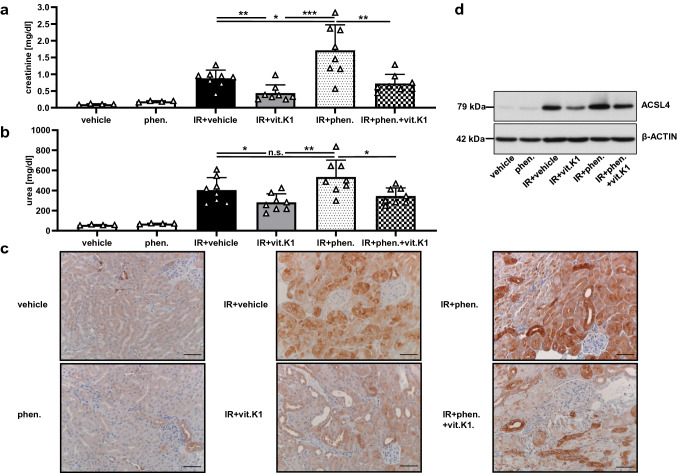
Fig. 5.
Vitamin K1 provides protection against renal ischemia–reperfusion injury, whereas phenprocoumon enhances the damaging effect. The significant therapeutic in vivo effect of vitamin K1 (vit.K1) and the detrimental effect of phenprocoumon (phen.) were evident under severe test conditions. All mice underwent 35 min of bilateral renal pedicle clamping followed by 48 h of reperfusion. Under these conditions, 15 min before ischemia, each mouse received a single intraperitoneal injection (total volume per mouse = 200 μl) of either PBS (vehicle), 4 mg phen./kg body weight, 25 mg vit.K1/kg body weight, or a combination as indicated (n = 4–8 mice per group as indicated). In this setting, we observed that the vehicle-treated mice in the IR group had significantly higher plasma levels of creatinine (a) and urea (b) than the vitamin K1-treated animals. In contrast, animals pretreated with phenprocoumon showed pronounced AKI, whereas phenprocoumon without IRI did not cause notable kidney function impairment. Remarkably, vitamin K1 when co-administered with phenprocoumon attenuated the extent of this phenprocoumon-mediated renal damage significantly. (c) Corresponding histological ACSL4 expression in the kidney samples of groups presented in (a) and (b). Increased expression of ACSL4 in this IR setting indicates an important role of ferroptosis in the complex pathology of acute tubular injury. ACSL4-positive tubuli and augmented ACSL4 expression can be seen in acute tubular injury (IR + vehicle group) and especially in the IR + phenprocoumon group, correlating with severe acute tubular damage. Normal renal parenchyma samples
taken from the vehicle and the phenprocoumon groups served as controls. The protective effect of vitamin K1 in this scenario, associated with decreased ACSL4 expression, is evident in the appropriately labeled groups (scale bars = 50 µm). d Analogous expression levels of ACSL4 in whole-kidney lysates taken from the different groups presented in (a) and (b). The indicated samples were obtained after reperfusion. Equal amounts of protein (20 µg/lane) were resolved by SDS-PAGE, and expression of ACSL4 was detected by western blotting. The blot was stripped and re-probed with an antibody against β-actin as a loading control