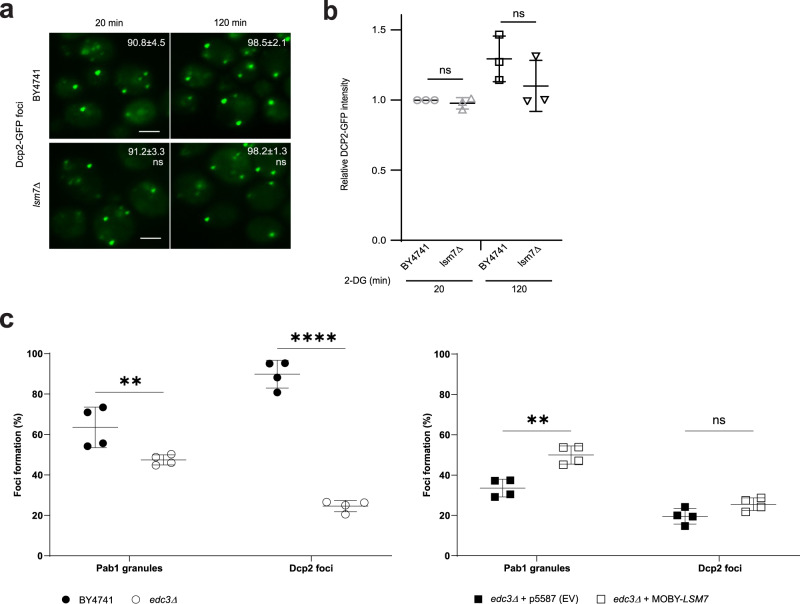
Fig. 3. Lsm7 impacts SG formation without affecting PB formation.
a PB formation is not significantly changed in the lsm7∆ mutant. WT (BY4741) and lsm7∆ mutant strains were treated with 2-DG for 20 min and 120 min, followed by sample collection and imaging. Values represent percentage of cells with Dcp2-GFP foci and are shown as mean ± S.D. Scale bar indicates 2 µm. Six biologically independent experiments were examined and >300 cells were analyzed for each (unpaired two-tailed t test). Left to right: ns = 0.8732, ns = 0.7548. b There is no statistically significant difference in the relative Dcp2-GFP signal intensity for the WT (BY4741) and the lsm7∆ mutant. Individual value points are shown with mean ± S.D. Three biologically independent experiments were examined for each strain and one representative image for each was analyzed for GFP signal (unpaired two-tailed t test). Left to right: ns = 0.1189, ns = 0.6956. c Overexpression of LSM7 can increase the 2-DG-induced SG formation in the SG- and PB-deficient edc3∆ mutant. Deletion of EDC3 results in a decrease in SGs (Pab1-RFP) and PBs (Dcp2-GFP), as compared to the WT (BY4741) (left). The SG phenotype can be partially rescued by overexpression of LSM7, without affecting the number of PBs, as compared to the empty vector control (right). Individual value points are shown with mean ± S.D of percentage of cells with Pab1-RFP granules and Dcp2-GFP foci. Four biologically independent experiments were examined and >200 cells were analyzed for each (two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test). Left to right: **p = 0.0014, ****p < 0.0001, **p = 0.0011, ns = 0.4091. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.