Fig. 2. Overview of the Hi-C-LSTM model.
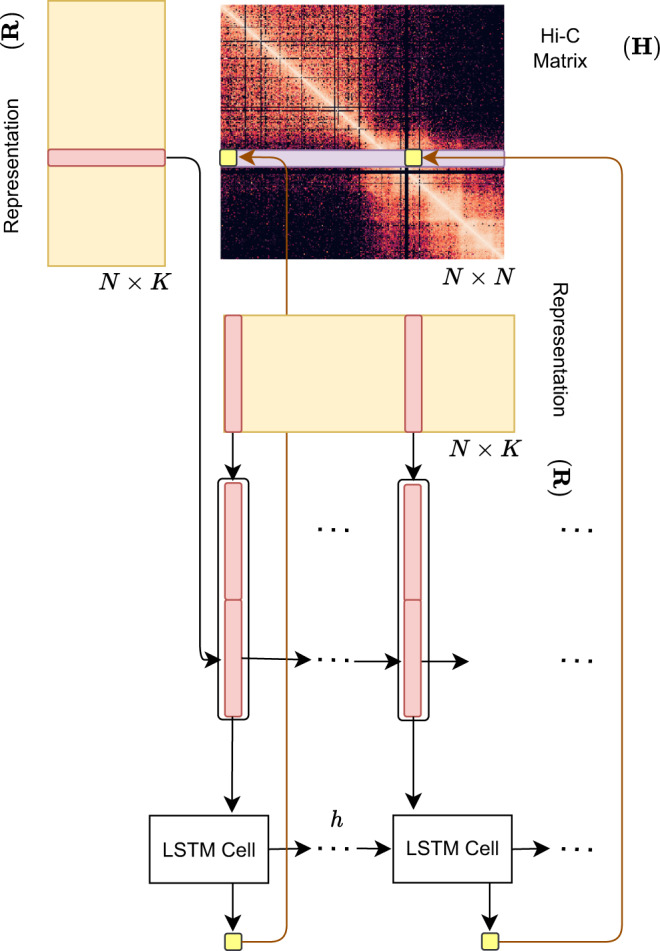
A trained Hi-C-LSTM model consists of a K-length representation Ri for each genomic position i and LSTM connection weights (see the “Methods” section). To predict the contact vector of a position i with all other positions, the LSTM iterates across the positions j ∈ {1…N}. For each (i, j) pair, the LSTM takes as input the concatenated representation vector (Ri Rj) and outputs the predicted Hi-C contact probability Hi,j. The LSTM hidden state h is carried over from (i, j) to (i, j + 1). This process is repeated for all N rows of the contact map by reinitializing the LSTM states. The LSTM and the representation matrix are jointly trained to minimize the reconstruction error.
