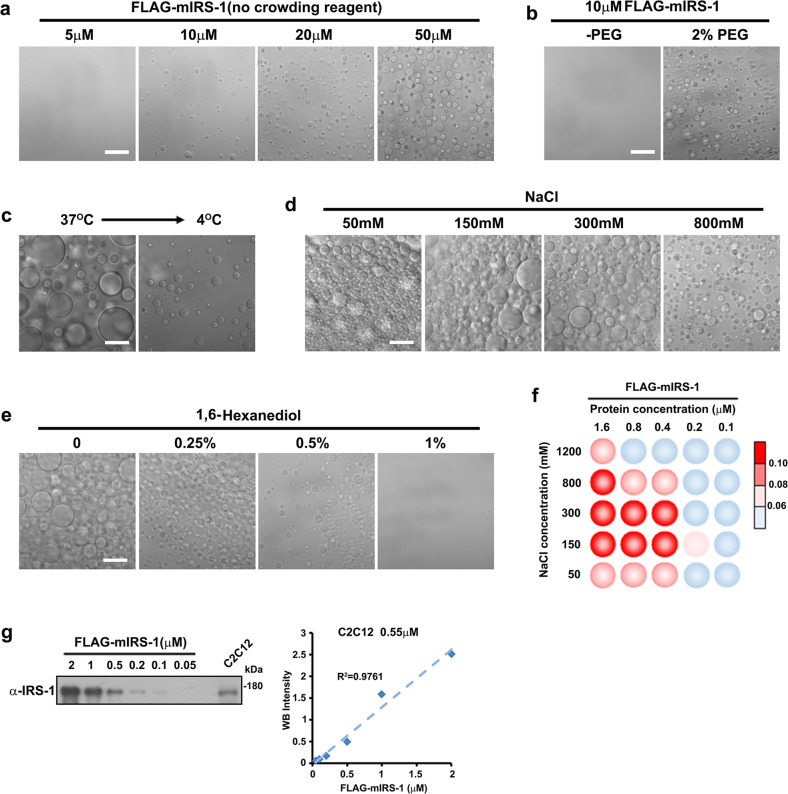
Fig. 2. IRS-1 undergoes phase separation in vitro.
a DIC images of FLAG-mIRS-1 LLPS at a series of protein concentrations (5–50 μM) (50 mM Tris-HCl pH 7.5, 10% glycerol, 1 mM DTT, 150 mM NaCl). The proteins were incubated with phase separation buffer at room temperature for 40 min. Scale bar, 20 µm. b DIC images of FLAG-mIRS-1 LLPS in the presence of molecular crowding (2% w/v PEG-8000) (right). No phase separation was observed without crowding agent (left). The proteins were incubated with phase separation buffer at room temperature for 5 min. Scale bar, 20 µm. c LLPS of mIRS-1 at 37 °C or 4 °C for 10 min. Scale bar, 20 µm. d DIC images of FLAG-mIRS-1 LLPS under different salinity, as indicated. The proteins (10 μM) were incubated with phase separation buffer at room temperature for 20 min. Scale bar, 20 µm. e DIC images of FLAG-mIRS-1 LLPS with the addition of 1,6-hexanediol at indicated concentration. The proteins (10 μM) were incubated with phase separation buffer at room temperature for 20 min. Scale bar, 20 µm. f Phase diagrams of GFP-mIRS-1 with concentrations ranging from 0.1-1.6 μM in 50 mM Tris (pH 7.5), 2% (w/v) PEG-8000, and sodium chloride (ranging from 50–1200 mM). Blue dots indicate no phase separation. Red dots indicate phase separation. The LLPS ability of mIRS-1 under different conditions was color-coded on the basis of droplet turbidity as measured at OD600 when the proteins had been incubated with phase separation buffer at 37 °C for 120 min. g Quantification result of endogenous IRS-1 protein concentrations in C2C12 cells based on immunoblot densitometry analysis performed on cell lysates and purified FLAG-mIRS-1 protein.