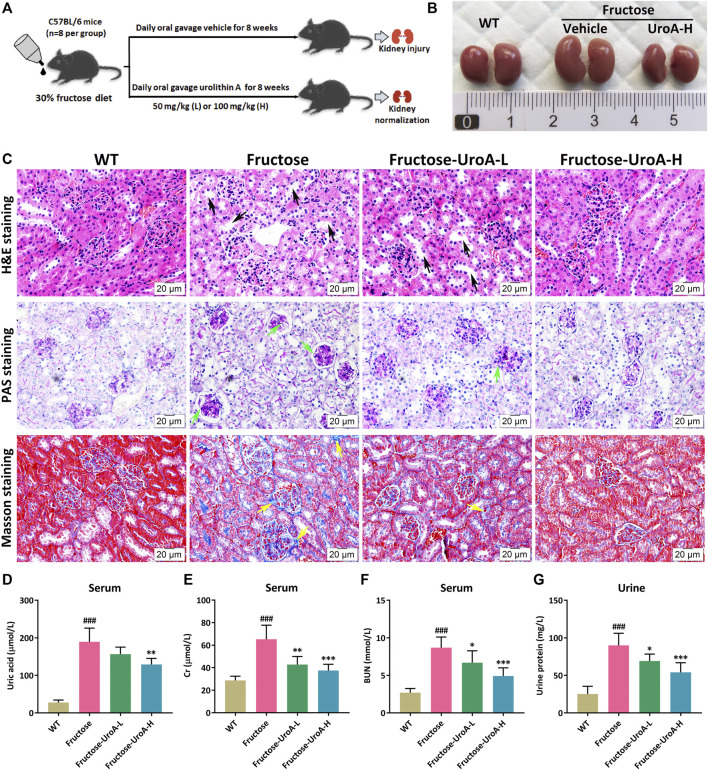
FIGURE 1.
Urolithin A (UroA) ameliorates fructose-induced hyperuricemic nephropathic in mice. (A) Study design. (B) Kidney macroscopic appearance. (C) Hematoxylin-eosin (H&E), Periodic Acid-Schiff (PAS), and Masson’s trichrome staining of kidney tissues from the wild-type (WT) or fructose-fed mice with intragastric administration of either vehicle or UroA, respectively (Scale bar: 20 μm). Fructose-fed mice showed obvious pathological changes in kidney tissues, including tubular hypertrophy and dilation (black arrow), glomerular basement membrane thickening (green arrow), and collagen deposition (yellow arrow). (D–G) Fructose-fed mice exhibited a decline in serum uric acid (D), creatinine (Gr) (E), blood urea nitrogen (BUN) (F), and urine protein (G) after receiving UroA treatment for 8 weeks. Mean ± S.D., n = 8. ### p < 0.001 versus the WT group; * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 versus the fructose group. UroA-L and UroA-H represent intragastric administration of urolithin A at low (50 mg/kg/day) and high (100 mg/kg/day) doses, respectively.