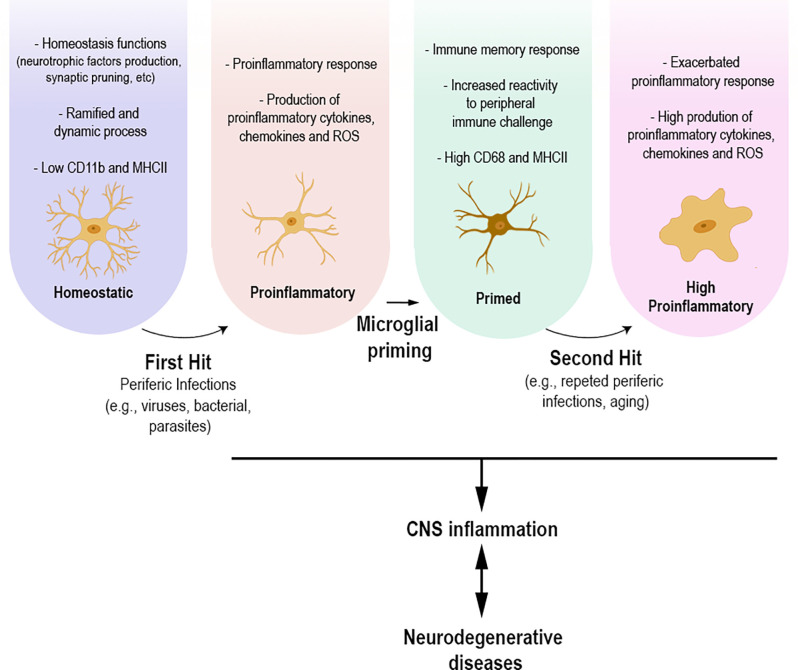
Figure 1.
Under physiological conditions, homeostatic microglial cells participate in various homeostasis functions, production of neurotrophic factors, and synaptic pruning. Their morphology presents ramified and dynamic cellular processes with high motility. Homeostatic microglia express low levels of CD11b and MHCII. Infections that occur throughout life, whether caused by viruses, parasites, or bacteria, can lead to microglial morphological and functional changes towards a proinflammatory state. The proinflammatory response leads to functional and morphological changes, including the upregulation of specific molecules and increased production of proinflammatory mediators, including cytokines, chemokines, and reactive oxygen species. Microglial cells present a branch architecture with thicker processes. This process can result in microglial priming, making these cells more responsive to an upcoming insult, causing an, even more, exacerbated inflammatory response. The different states of microglia are directly related to the inflammation process, which in turn might be related to the development of neurodegenerative diseases.