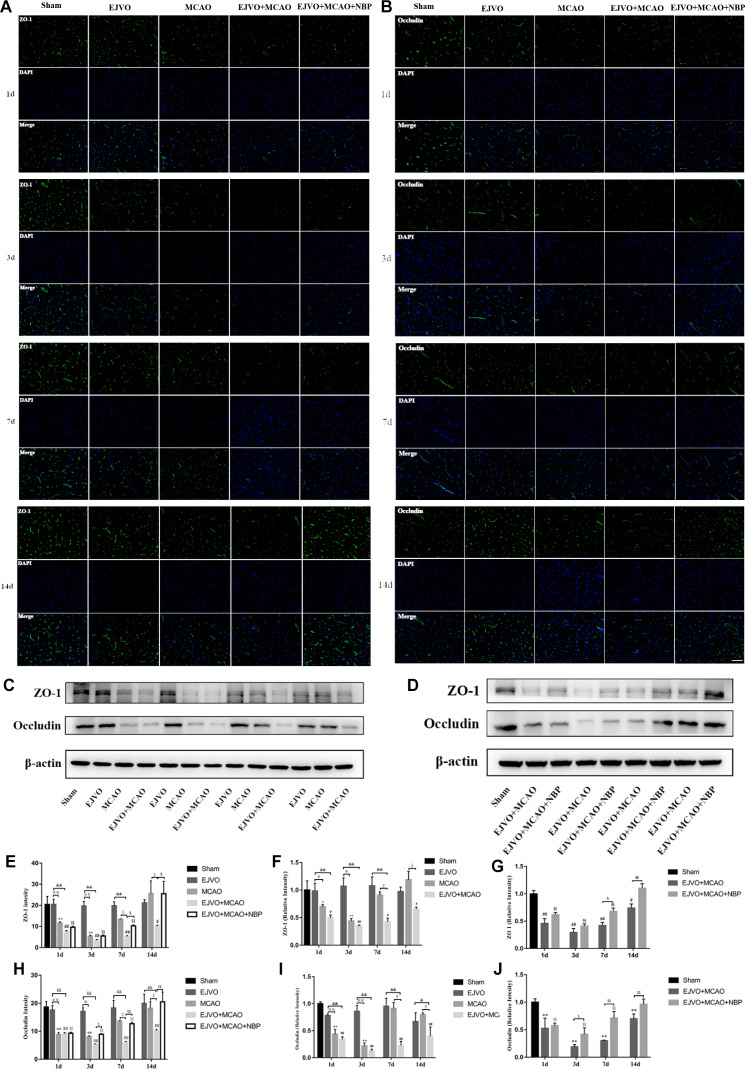
Figure 9.
Cerebral venous circulation disturbance accelerate BBB damage, and NBP attenuated damage of BBB caused by MCAO plus with EJVO. (A) Expression of ZO-1 in the ischaemic area or corresponding region measured by immunofluorescence staining. (B) Expression of occludin in the ischaemic area or corresponding region measured by immunofluorescence staining. (C, D) Expression of ZO-1 and occludin detected by Western blot in the ischaemic brain tissue or corresponding area in the sham or EJVO group. (E) Quantification analysis of ZO-1 analysed by immunofluorescence staining. (F, G) Quantification analysis of ZO-1 analysed by Western blot. (H) Quantification analysis of occludin analysed by immunofluorescence staining. (I, J) Quantification analysis of occludin analysed by Western blot. data are presented as mean±SD, n=5 per group for immunofluorescence staining and n=3 per group for Western bolt. *P<0.05, MCAO vs sham; **p<0.01, MCAO vs sham; #p<0.05, EJVO +MCAO vs Sham; ##p<0.01, EJVO +MCAO vs sham; §§P<0.01, EJVO +MCAO + NBP vs sham; ※p<0.05, MCAO vs EJVO; ※※p<0.01, MCAO vs EJVO; &p<0.05, EJVO +MCAO vs EJVO; &&p<0.01, EJVO +MCAO vs EJVO; ∫∫p<0.05, EJVO +MCAO vs MCAO; $p<0.05, EJVO +MCAO + NBP vs EJVO +MCAO; $$p<0.01, EJVO +MCAO + NBP vs EJVO +MCAO. Scale bar=50 µm. BBB, blood-brain barrier; EJVO, external jugular vein occlusion; MACO, middle cerebral artery occlusion; NBP, Dl-3-n-butylphthalide.