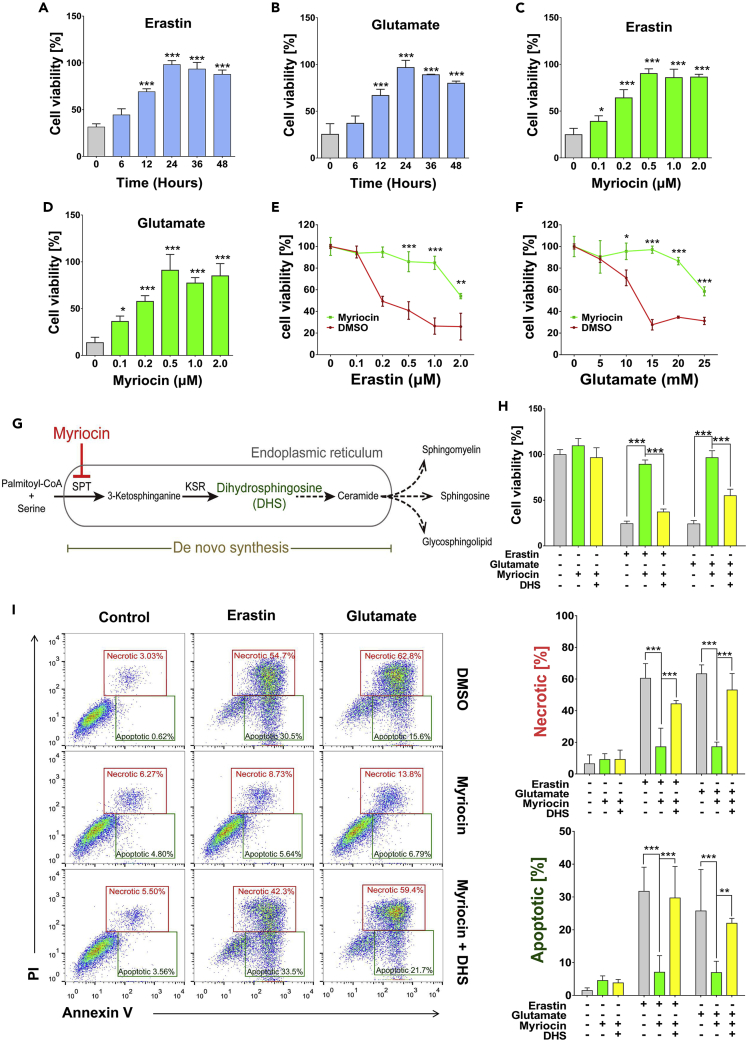
Figure 1.
Myriocin inhibits erastin- or glutamate-induced ferroptosis in HT22 cells
(A and B) Cell viability analysis of cells pre-treated with myriocin (0.5 μM) for indicated time before incubating with erastin (1 μM) (A) or glutamate (15 mM) (B) for 24 h.
(C and D) Cell viability analysis of cells pre-treated with indicated concentrations of myriocin for 36 h before incubation with erastin (1 μM) (C) or glutamate (15 mM) (D) for 24 h.
(E and F) Cell viability analysis of cells pre-treated with or without myriocin (0.5 μM) for 36 h before incubating with indicated concentrations of erastin (E) or glutamate (F) for 24 h.
(G) Schematic diagram of the de novo biosynthesis pathway of sphingolipids in the ER SPT (serine palmitoyl transferase), and KSR (3-ketosphinganine reductase).
(H) Cell viability analysis of cells pre-treated with or without myriocin (0.5 μM) or DHS (1 μM) for 36 h before incubating with or without erastin (1 μM) or glutamate (15 mM) for 24 h.
(I) Annexin V-FITC/PI flow cytometric analysis of cells pre-treated with or without myriocin (0.5 μM) or DHS (1 μM) for 36 h before incubating with or without erastin (1 μM) or glutamate (15 mM) for 24 h. Histograms show numbers of necrotic and apoptotic cells. For the above, error bars represent the mean ± SD (n = 3, ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001).