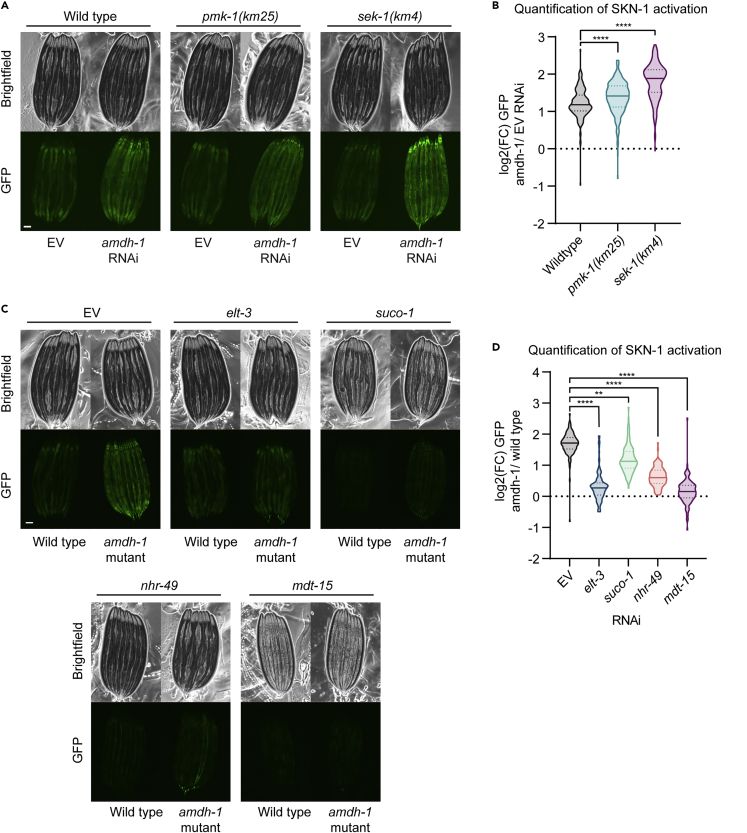
Figure 2.
Genetic requirements of SKN-1 activation upon perturbation of histidine catabolism
(A) Fluorescent images of SKN-1 reporter animals in a wildtype, sek-1(km4) or pmk-1(km25) mutant animals fed amdh-1 RNAi. Scale bar, 100 μm.
(B) Quantification of SKN-1 activation (amdh-1 RNAi normalized to median of EV) from (A), Data shown are representative of n = 3 biological replicates with n > 172 animals per condition for each replicate. ∗∗∗∗ = p < 0.0001 using a one-way ANOVA.
(C) Fluorescent images of SKN-1 reporter animals in a wildtype or amdh-1(uth29) mutant background fed RNAi targeting elt-3, suco-1, nhr-49, and mdt-15. Scale bar, 100 μm.
(D) Quantification of SKN-1 activation (amdh-1 mutant normalized to median of wild type) from (C), Data shown are representative of n = 3 biological replicates with n > 88 animals per condition for each replicate. ∗∗ = p < 0.01, ∗∗∗∗ = p < 0.0001 using a one-way ANOVA.