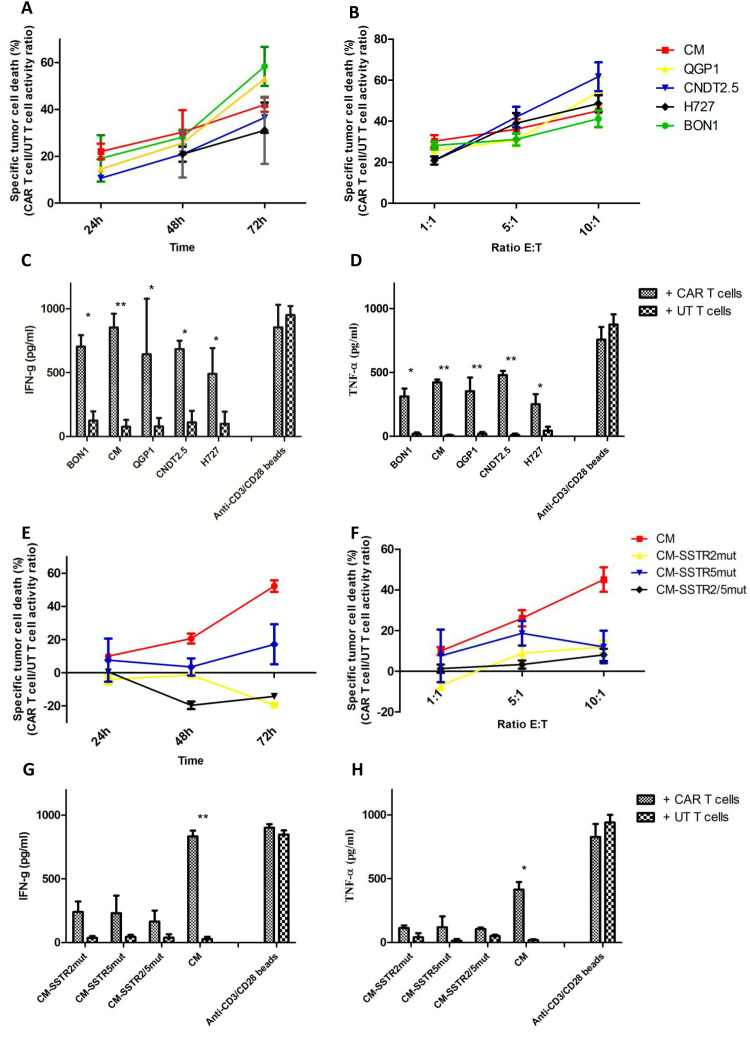
Figure 3.
Anti-SSTR CAR T cells exhibit antigen-specific tumoricidal activity. (A) Anti-SSTR CARs endow human T lymphocytes with reactivity against SSTR-expressing targets. By in vitro BLI assay, CAR T cells induced cell death in up to 58% of Luc+ NET cell lines as compared with UT T cells at an E:T ratio of 1:1. The percentage of specific tumor cell lysis was calculated as the ratio between CAR T cell and UT T cell antitumor activity using the formula: % lysis=1-(mean BLI signal in the presence of anti-SSTR CAR T cells/mean BLI signal in the presence of UT cells) x 100%. (B) In vitro BLI assay to evaluate the cytolytic activity of CAR T cells as compared with UT T cells according to increasing E:T ratios after 24 hours of coculture with NET cells. The degree of cytotoxicity induced by CAR T cells increased when the number of effector cells increased. (C) IFN-γ and (D) TNF-α release on 24 hours coculture of NET cells with CAR T cells or UT T cells at an E:T ratio of 1:1. Cytokine production was measured in culture supernatants by ELISA. CD3/CD28 T cell stimulation through TransAct was used for positive control experiments. (E) In vitro BLI assay to investigate the cytolytic activity of CAR T cells as compared with UT T cells against mutant CM cells and parental cells at an E:T ratio of 1:1. (F) Evaluation of the cytotoxic potential of CAR T cells against CM cells harboring wild-type or mutated SSTR2 and/or SSTR5 according to increasing E:T ratios after 24 hours of coculture. (G) IFN-γ and (H) TNF-α release on 24 hours coculture of CAR T cells or UT T cells with mutated or parental CM cells at an E:T ratio of 1:1. All experiments were carried out in technical triplicate using lymphocytes from three healthy donors. Mean values and standard errors are represented in figure. *P<0.05, **p<0.01. CAR, chimeric antigen receptor; E:T, effector:target; NET, neuroendocrine tumor; SSTR, somatostatin receptor; UT, untransduced.