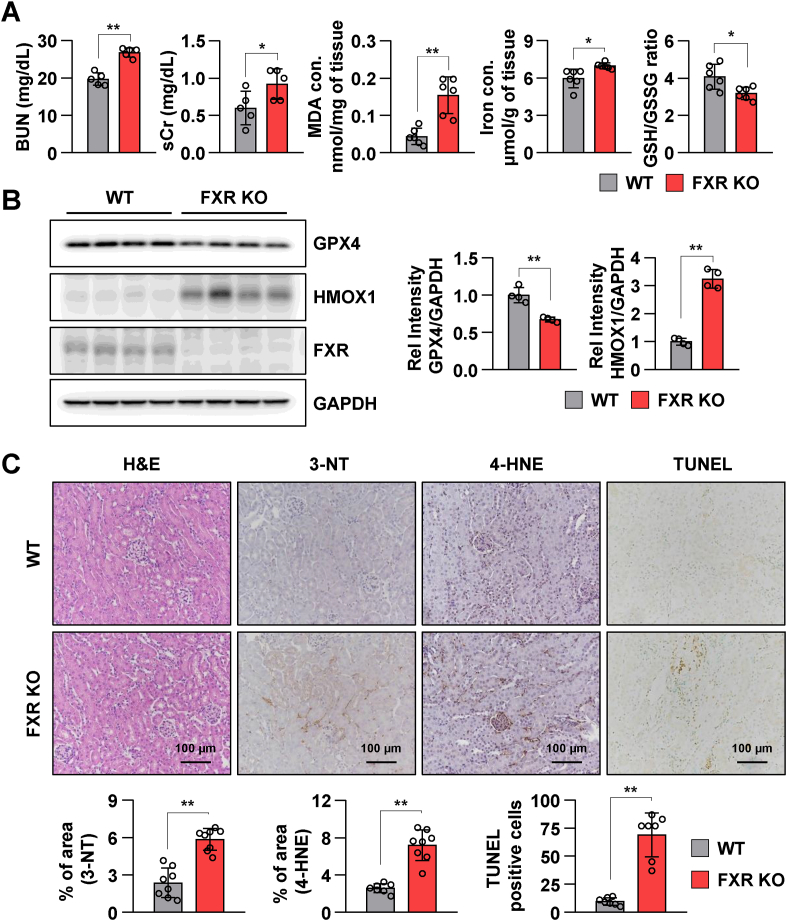
Fig. 2.
FXR deficiency promotes renal injury and ferroptotic responses in mice.
The serum and kidney tissues were collected from wild-type (WT) and FXR knockout (FXR KO) mice (n = 6). (A) Serum BUN and Cr levels of each group. Malondialdehyde (MDA) and iron levels as well as GSH/GSSG ratio in kidney tissues. (B) Protein levels of GPX4, HMOX1, and FXR were detected by immunoblotting. The relative protein levels are shown. The values for the WT group were set to 1. (C) Representative images of hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining to examine the histology and immunohistochemistry to examine the expression of 3-NT and 4-HNE. Computer-based morphometric analysis is shown (bar graph, n = 8 in each group). Representative image of TUNEL staining. Quantitative analysis of positive TUNEL staining is shown (n = 7). Scale bar, 100 μm. All values are presented as the mean ± SD. Statistical significance was measured using one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc-test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.005.