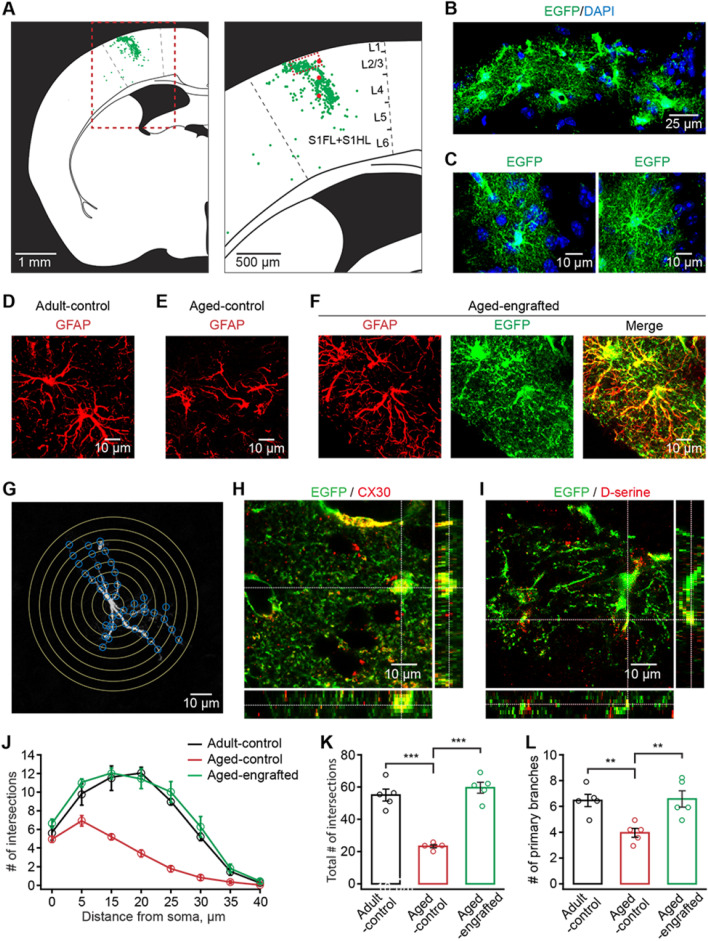
Fig. 2.
Engrafted in-vitro-generated GPCs achieve long-term morphological integration and remain morphologically younger in the aged neocortex. A Representative dot map showing the distribution of engrafted GPC-derived astrocytes 12 months after transplantation (left panel, the coronal section of the half brain; right panel, primary somatosensory cortex outlined by the red dashed line in the left panel. 3 red points indicate cell transplantation points. S1FL: primary somatosensory cortex, forelimb region; S1HL: primary somatosensory cortex, hindlimb region.). Engrafted GPC-derived astrocytes were distributed in different cortical layers in the somatosensory cortex. B, C Representative images of engrafted GPC-derived astrocytes, positive for EGFP, 12 months after transplantation B the network of astrocytes outlined by the red line in the right panel of A. C Higher magnification of single astrocytes showing the complex fine structures of engrafted GPC-derived astrocytes). D–F Representative confocal 3-dimensional reconstructed images showing GFAP-immunoreactive astrocytes in adult-control (D), aged-control, (E) and aged-engrafted mice groups (F). Engrafted astrocytes are also labeled with EGFP protein (F). G Sholl analysis for the measurement of the relative number of astrocyte processes. The morphology of an astrocyte was traced and outlined from the GFAP labeling (white). Concentric rings (yellow) were placed 5 µm apart around the cell. Branching points, where astrocytic processes made intersections (blue) with a concentric ring, were used to quantify the relative number of processes. H, I Engrafted GPC-derived astrocytes express the gap junction protein (H), connexin 30 (CX30), and the gliotransmitter, D-serine (I) 12 months after transplantation. Z-stack imaging showing the co-localization of CX30 or D-serine with the EGFP positive engrafted astrocytic soma or processes. J Single astrocyte Sholl analysis showing the number of intersections of astrocytic branches and branchlets with concentric spheres centered in the middle of cell soma (n = 20–25 cells from 5 mice for each group). K, L Summary of total the intersection number (K) and primary branches number (L) in adult-control, aged-control, and aged-engrafted mice groups (n = 20–25 cells from 5 mice for each group; total number of intersections: adult-control versus aged-control, P = 1.90 E−5; aged-control versus aged-engrafted, P = 4.29 E−6; number of primary branches: adult-control versus aged-control, P = 0.0116; aged-control versus aged-engrafted, P = 0.0086; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc comparisons test). All data in the figure are shown as mean ± s.e.m