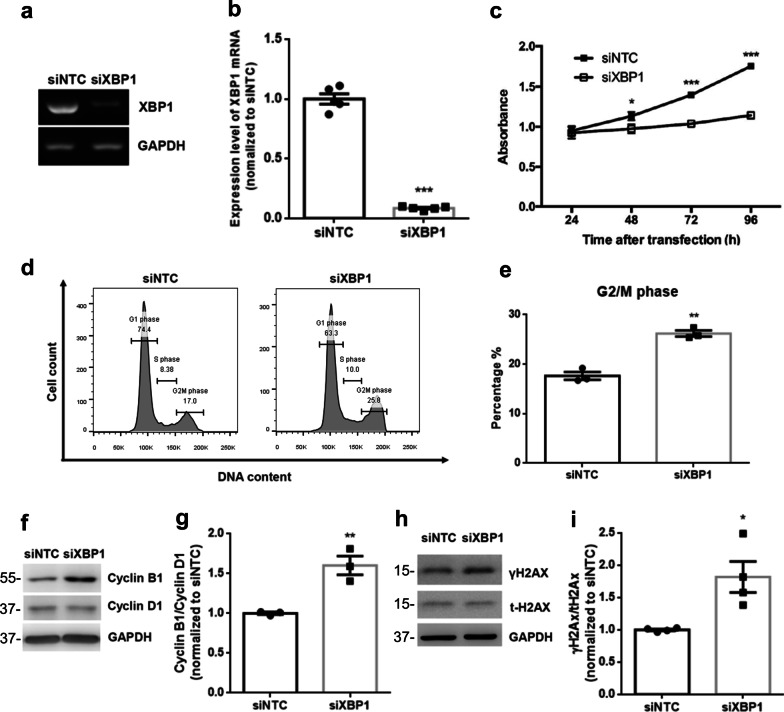
Fig. 5.
Knockdown of XBP1 induces cell cycle G2/M arrest in HK2 renal tubule epithelial cells. a and b The knockdown efficiency of XBP1 was determined by reverse transcription-PCR and quantified. siNTC: negative control siRNA. c Loss of XBP1 results in growth inhibition. MTS assay was conducted every 24 h for up to 4 days to examine the effect of XBP1 deficiency on the growth rate of cells based on the absorbance. d Loss of XBP1 results in modulating the cell cycle. Cells were transfected with siNTC or siXBP1. After 24 h, cells were harvested and subjected to flow cytometric analysis to determine the cell cycle distribution. e The amounts of cells in the G2/M phase of the cell cycle in HK2 cells following transfection of indicated siRNA were quantified. f Western blot analysis showed the expression of cyclin B1 and cyclin D1 proteins. GAPDH was used as an internal control. g The ratio of cyclin B1 to cyclin D1 in HK2 cells following transfection of indicated siRNA. h Western blot analysis showed the expression of γH2AX and t-H2AX proteins. i The ratio of γH2AX to t-H2AX in HK2 cells following transfection of indicated siRNA. Data are expressed as means ± SEM of three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001, as compared with siNTC group