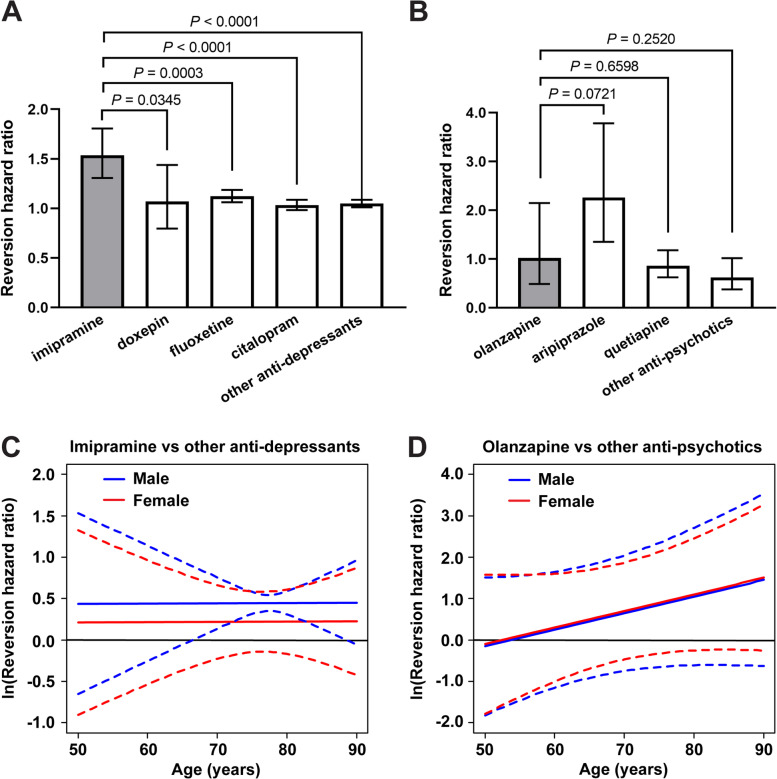
Fig. 5.
Mixed medication and interaction models evaluating clinical diagnosis reversion. a The hazard ratio of clinical diagnosis reversion toward normal was plotted comparing the cumulative drug exposure of imipramine, doxepin, fluoxetine, citalopram, or all other antidepressants to being off the medication, in the same subjects. The data indicate the hazard ratio ± 95% CI. Imipramine was compared to each other group and all P values are shown. b The hazard ratio of clinical diagnosis reversion toward normal was plotted comparing the effect of being on olanzapine, aripiprazole, quetiapine, or all other antipsychotics to being off the medication, in the same subjects. The data indicate the hazard ratio ± 95% CI. Olanzapine was compared to each other group and all P values are shown. c Imipramine was compared to other antidepressant medications for the potential effect of cumulative drug exposure on the hazard ratio of clinical diagnosis reversion toward normal, with age and sex considered as interaction variables. The data represent the natural log of the HR (solid lines) and 95% CI (dotted lines). Statistical significance is reached when the 95% CI does not include zero, which occurs from 66.5 to 88.5 years of age in males. d Olanzapine was compared to other antipsychotic medications for the potential effect of being on the medication on the hazard ratio of clinical diagnosis reversion, with age and sex considered as interaction variables. The data represent the natural log of the HR (solid lines) and 95% CI (dotted lines)