Figure 1.
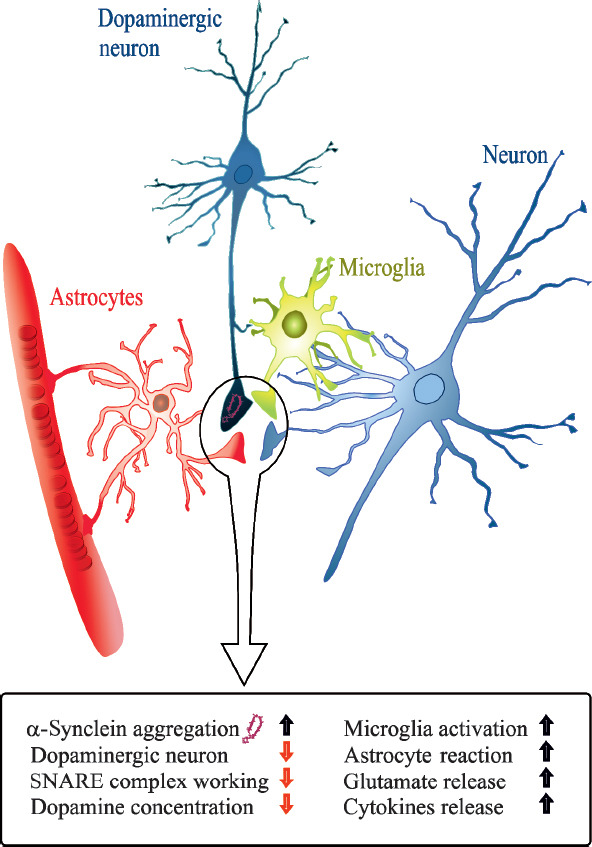
The inflammatory mechanism induced by alpha-synuclein accumulation.
Formation of toxic α-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease (PD), specifically at the presynaptic terminal, leads to changes of proteins involved in synaptic transmission (i.e., SNARE complex alteration and increased glutamate release), determining synaptic dysfunction and contributing to degeneration of dopaminergic neurons. Moreover, α-synuclein aggregation could be considered as a causal link between neurodegeneration and neuroinflammation in PD, inducing astrocyte and microglia reaction, consequent release of cytokines and activation of adaptive immune system. SNARE: Soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive fusion protein attachment protein receptor.
