Figure 1.
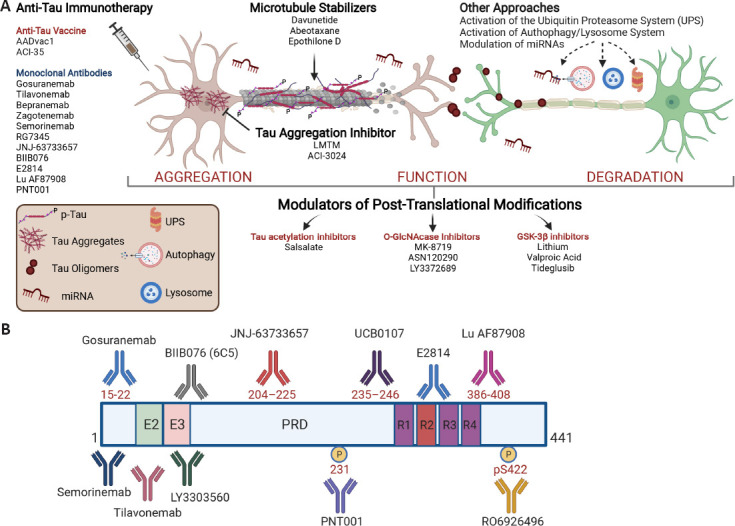
Scheme showing point of attack of different pharmacological classes of anti-tau drugs and epitope locations on the primary sequence of tau, for antibodies currently in clinical trials.
Domain structural features are shown for the longest isoform of tau (2N4R, 441 amino acids). The 2N4R isoform contains two N-terminal domains (N1 and N2 of 29 amino acid each), two proline-rich domains (P1 and P2 of 46 amino acid each), and four microtubule-binding domains (R1–R4 of 31 amino acid each). E2 and E3 represent exon 2 and exon 3, respectively; PRD is the proline-rich domain; R1–R4 represent the microtubule binding regions, including R2 encoded by exon 10. 2N4R: Human tau-441; GSK3β: glycogen synthase kinase-3beta; LMTM: leuco-methylthioninium bis (hydromethanesulfonate); PRD: proline-rich sequence recognition domains; UPS: ubiquitin proteasome system.
