Figure 3.
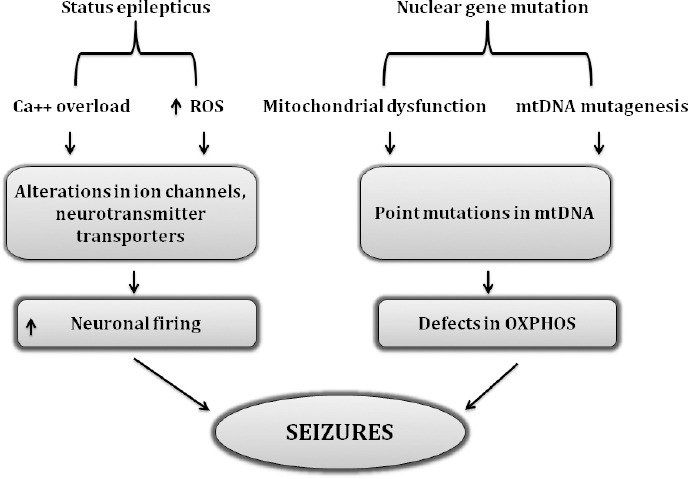
Association of mutational modifications and ROS-related cascade in deterioration of epileptic seizures.
Flow chart indicates the role of nuclear mutations in inducing mitochondrial dysfunction, point mutations in mtDNA ultimately producing defects in OXPHOS machinery which is considered as a prime culprit responsible for causing mitochondrial dysfunction and related changes. On the other hand, the common pathways involved in the initiation of status epilepticus are still the enhanced oxidative load and dysregulation of calcium hemostasis with the result of massive neuronal firing and seizure indicating that these two pathways share common crosstalk in epileptic seizures. Ca++: Calcium overload; mtDNA: mitochondrial DNA; OXPHOS: oxidative phosphorylation; ROS: reactive oxygen species.
