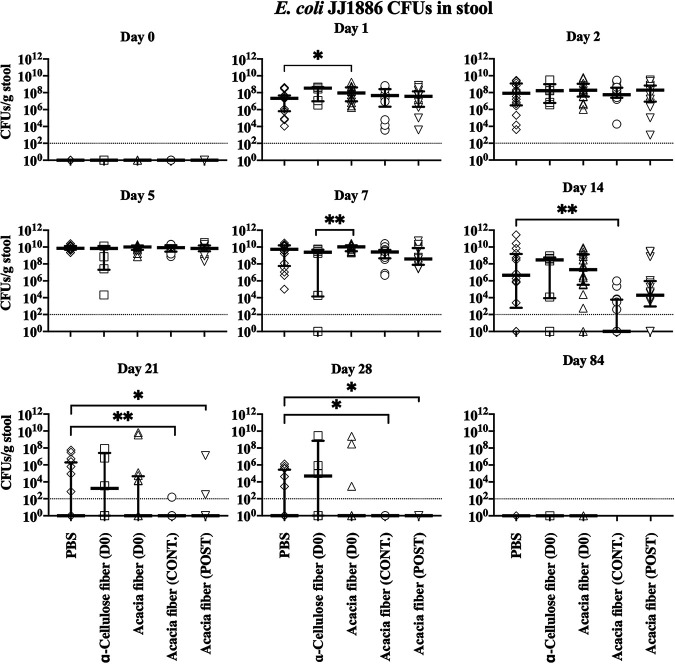
FIG 2.
Soluble acacia fiber treatment decreased colonization by pathogenic E. coli JJ1886 in the murine gut despite clindamycin selective pressure. Mice were treated with clindamycin from –2 to 1 day postchallenge and challenged with 107 CFU E. coli JJ1886 on day 0. Mice were given acacia fiber (soluble), α-cellulose fiber (insoluble), or PBS by oral gavage once at the time of infection (D0), for 18 days (CONT.), or for 4 days postchallenge (POST) (n = 16 per group except n = 6 for the α-cellulose fiber group). Data are medians ± interquartile range. Limit of detection (dotted line) = 102 CFU/g stool. *, P ≤ 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.01; two-tailed Mann-Whitney test.