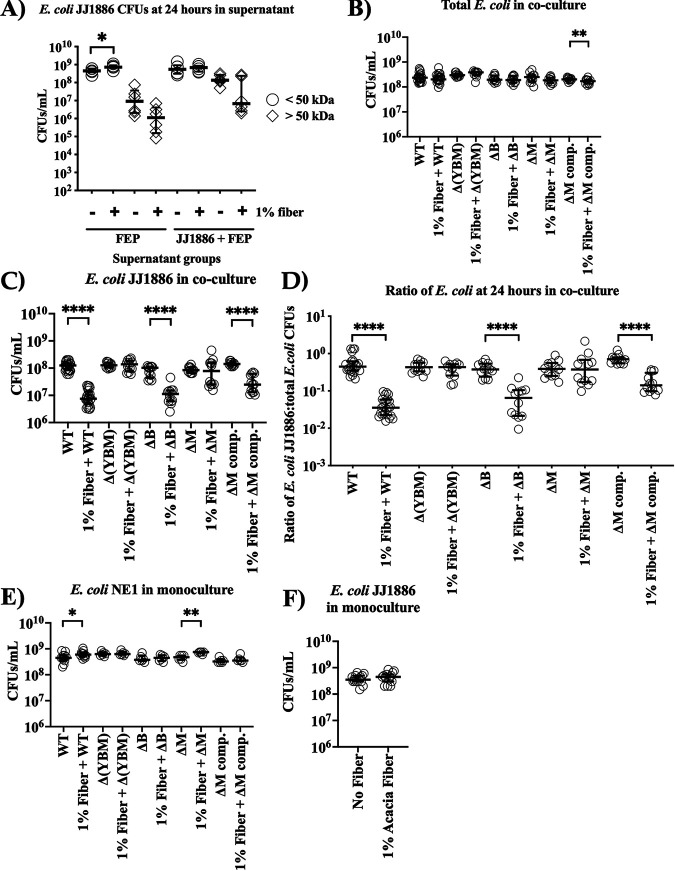
FIG 5.
Native gut E. coli inhibited pathogenic E. coli JJ1886 with colicin M in the presence of acacia fiber. (A) E. coli NEC monoculture and coculture with E. coli JJ1886 were grown at a final concentration of 3 × 106 CFU/mL with ± 1% (wt/vol) acacia fiber. Culture supernatant fractions smaller or larger than 50 kDa were incubated with E. coli JJ1886 at a final concentration of 3 × 106 CFU/mL (n = 6 per condition). (B to F) E. coli NE1 ΔB, ΔM, and Δ(YBM) denote disrupted colicin activity genes cba, cma, or cya, cba, and cma, respectively. A final concentration of 3 × 106 CFU/mL was used for E. coli JJ1886, E. coli NE1 wild type (WT) or mutant, or both. (B to D) E. coli JJ1886 was cocultured with ± 1% (wt/vol) acacia fiber and E. coli NE1 WT (n = 24), E. coli NE1 colicin knockout mutants (ΔYBM, ΔB, or ΔM) (n = 12), or E. coli NE1 ΔM complement (ΔM comp.) (n = 12). (D) CFU were enumerated by plating on nonselective (B) and selective (C) agar plates to determine the ratio of E. coli JJ1886:total E. coli. (E and F) E. coli monocultures with ± 1% (wt/vol) acacia fiber were performed in parallel as growth controls [n = 12, E. coli NE1 WT; n = 6, E. coli NE1 ΔB, ΔM, Δ(YBM)], and ΔM comp.; n = 15, E. coli JJ1886). Monoculture CFU were enumerated by plating on nonselective agar plates. Data are medians ± interquartile range. *, P ≤ 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.01; ****, P ≤ 0.0001; two-tailed Mann-Whitney test.