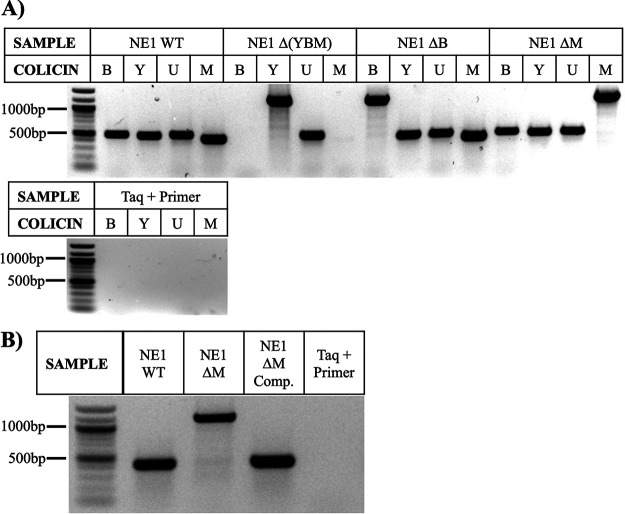
FIG 6.
Confirmation of colicin knockout and complement E. coli NE1 strain construction. (A) A zeocin selective marker (776 bp) was inserted into the colicin activity genes harbored by E. coli NE1 wild-type (WT) bacteria. E. coli NE1 ΔB, ΔM, and Δ(YBM) denote disrupted colicin activity genes cba, cma, or cya, cba, and cma, respectively. Plasmid DNA was extracted, PCR amplified with primers targeting colicin activity genes, and visualized. Increased product size indicated successful insertion of the zeocin construct. Absent bands suggested off-target loss of the respective colicin activity gene. DNA sequencing confirmed nonspecific binding of published colicin U primers to colicin Y. E. coli NE1 WT served as the positive control. The Taq polymerase, primers, and water were run as a negative control. (B) E. coli NE1 ΔM comp. denotes the E. coli NE1 ΔM complement strain that was transformed with pTO4 containing colicin M activity (cma) and immunity (cmi) genes. Plasmid DNA was extracted, amplified, and visualized as described in panel A. Successful addition of cma into E. coli NE1 ΔM comp. resulted in a decreased product size equivalent to that of E. coli NE1 WT.