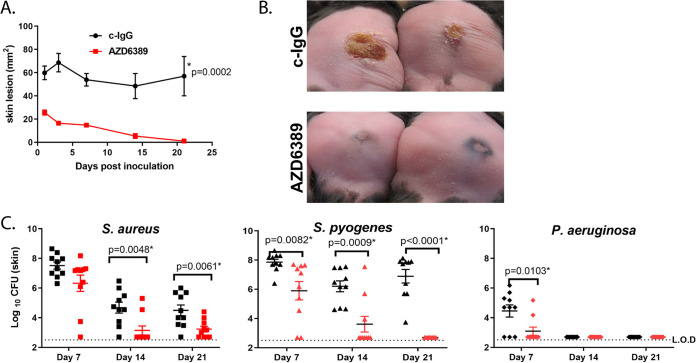
FIG 3.
Targeting a single pathogen with AZD6389 accelerates polymicrobial wound closure. Diabetic mice (n = 10 per group) were passively immunized with AZD6389 (15 mg/kg each MAb) or c-IgG (15 mg/kg) and challenged 24 h later with S. aureus SF8300 (1.0 × 107 CFU)/P. aeruginosa (1.0 × 105 CFU)/S. pyogenes (10 CFU). (A) Skin lesion sizes were measured at indicated times and graphed as mean values ± SEM. Statistical difference between c-IgG and AZD6389 group was determined using a Vardi’s AUC test (two sample tests for growth under the curve dependent right censoring) and considered statistically different if P < 0.05 as indicated with a (*). (B) Representative pictures of skin lesions 21 days after challenge. (C) Bacteria CFU in lesions at indicated times postchallenge. Data represent mean values ± standard deviation (error bars). Statistical difference for CFU between both group was analyzed with a Mann-Whitney test, and considered statistically different if P < 0.05 as indicated with a (*).