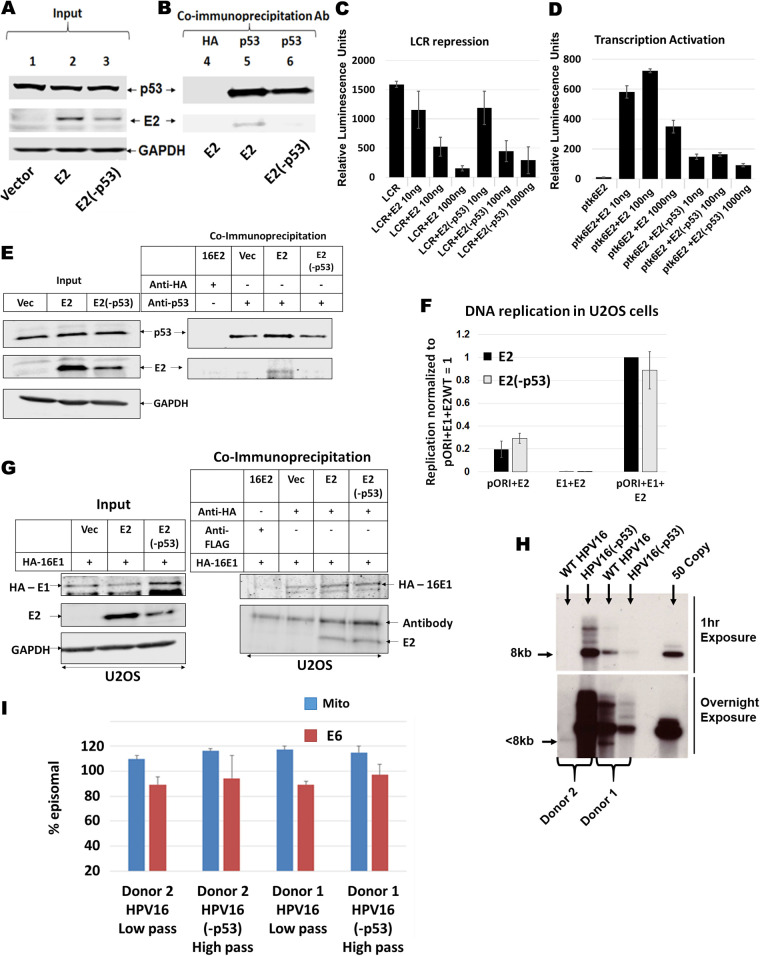
FIG 3.
Generation and characterization of p53 binding mutant of HPV16 E2 (E2-p53) in N/Tert-1 cells. (A) Input Western blot of stably expressing E2 and E2(-p53) in N/Tert-1 Cells. For E2(-p53), residues W341, D344 and D338 were mutated to alanine as previously described (42, 43). (B) Co-immunoprecipitation pull down of E2 using polyclonal antibody against p53. (C) HPV16 long control region repression assay of wild-type E2 and E2(-p53). N/Tert-1 cells were transiently transfected with 1 μg pHPV16-LCR-Luciferase reporter plasmid along with 10 ng, 100 ng, or 1000 ng of E2 or E2(-p53) plasmid. (D) E2 transcriptional activity assay of wild-type E2 and E2(-p53). Similar to LCR repression assay, N/Tert-1 cells were transiently transfected with 1 μg pTK6E2-Luciferase reporter plasmid along with increasing amounts of E2 wild-type and E2(-p53) plasmids. For (C) and (D), relative luminescence units were calculated by normalizing absolute luminescence readouts to input protein concentration. (E) U2OS cells stably expressing E2-WT and E2(-p53) were generated and a p53 co-immunoprecipitation carried out. Left panel, input; right panel, co-IP. (F) Transient DNA replication assays were carried out on U2OS cells transfected with pOri, E1 or the indicated E2. Both E1+E2-WT and E1+E2(-p53) increased replication similarly, both significantly above background. (G) HA tagged E1 was transfected into the indicated cell lines and a HA co-immunoprecipitation carried out. Left panel, input; right panel, co-IP. (H) Southern blot of SphI digested DNA (cuts the HPV16 genome once) from the indicated immortalized human foreskin keratinocytes. An over exposure of this blot indicated a band in Donor 2 wild-type cells that migrated around 7.5kbp, indicating a part of the genome may have been lost during immortalization. PCR demonstrates that viral DNA is in these cells, and they are immortalized. With donor 1 there is less DNA with the mutant genome than the wild type, the opposite of Donor 2. Therefore, the mutation did not trend toward influencing the levels of DNA in the immortalized HFK. (I) TV exonuclease digestion assay to determine viral genome status. We looked at GAPDH in this assay and called the ΔCt for GAPDH 100% degradation, then we estimated the resistance of both mitochondrial (mito) DNA and HPV16 (E6) to degradation. In all cases the HPV16 DNA is predominantly episomal. As an example, if the ΔCt for GAPDH was 10 following exonuclease treatment, and the ΔCt for mito and E6 equals 1, then they were estimated as 90% episomal DNA (mitochondria have circular genomes that are resistant to the exonuclease). Low pass indicates low passage, 7 or less. High pass indicates high passage, 12 or greater. This demonstrates that, even following prolonged culture, there is no shift toward integration of the HPV16 genomes. The results shown are from duplicate or triplicate experiments, and standard error bars are shown.