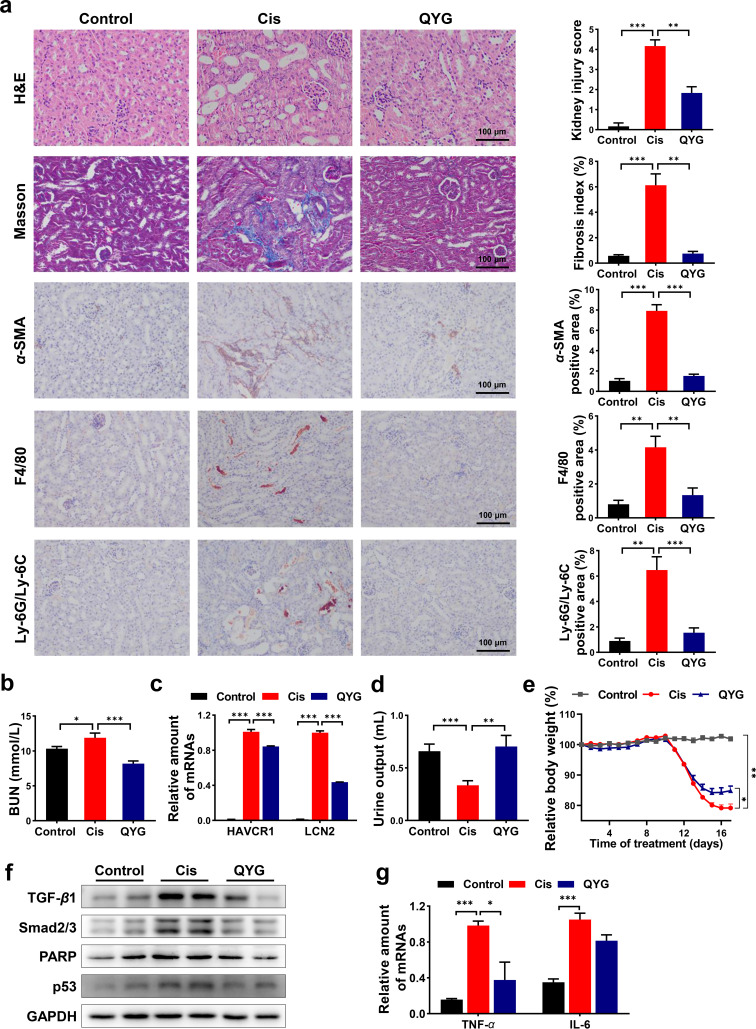
FIG 1.
QYG attenuated cisplatin-induced AKI, improved renal function, and inhibited potential mediators of cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity. (a) Kidney obtained from treated mice was examined with H&E staining, Masson’s trichrome staining, and IHC against α-SMA, F4/80, and Ly-6G/Ly-6C. Photomicrographs were captured at a magnification of 200×. Kidney injury score and fibrosis index were semiquantitatively scored based on the criteria we set. Positive stained area of IHC was quantified using ImageJ. (b) Concentration of BUN in serum was detected using commercial kit. (c) mRNA levels of HAVCR1 and LCN2 in kidney were analyzed by qPCR, and relative gene expression was expressed as relative fold change compared to Cis group. (d) Urine output volume of mice was measured for 12 h before sacrifice. (e) Relative body weight of mice in each group was recorded throughout the experiment. (f) Total protein expression of TGF-β1, Smad2/3, PARP, and p53 in kidney. GAPDH (glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase) was used as a loading control. (g) mRNA levels of TNF-α and IL-6 in renal tissue. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 8). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; and ***, P < 0.001.