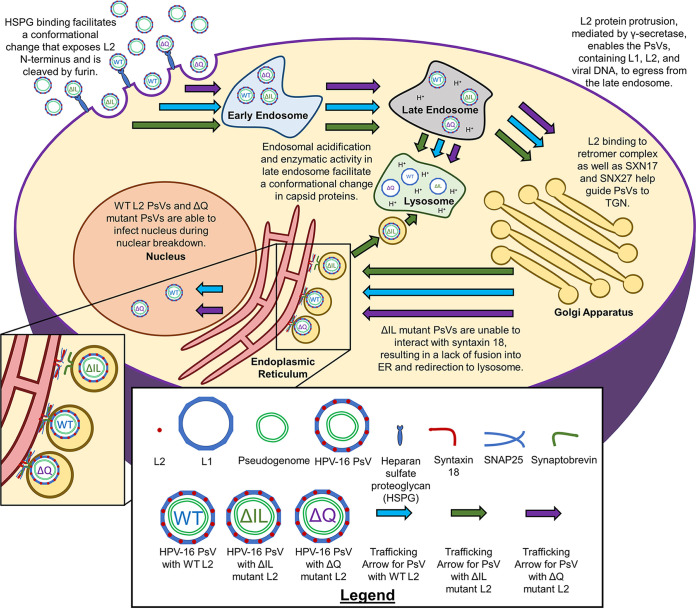
FIG 11.
Cartoon model of proposed HPV16 trafficking. HPV16 PsVs enter the cell upon HSPG binding and furin cleavage of the exposed L2 N-terminus. PsVs travel to the early endosome, followed by the late endosome. The acidic pH of the late endosome and enzymes facilitate a conformational change in the capsid proteins. Some of the L1 protein is sent to the lysosome for degradation. The L2 protein facilitates the movement from the late endosome and retrograde trafficking to the trans-Golgi network, as well as the rest of the Golgi apparatus. L2 embeds itself into the endosome vesicle through mediation by γ-secretase, which facilitates the interaction with sorting proteins such as retromer, SNX17, and SNX27. PsVs approach the ER membrane and interact with syntaxin 18, allowing for vesicular fusion into the ER before nuclear breakdown during mitosis. The WT and ΔQ mutant PsVs infect the nucleus and deposit the pseudogenome. However, ΔIL mutant PsVs are unable to interact with syntaxin 18 and, thus, are unable to progress past the ER and are redirected to the lysosome.