Figure 7.
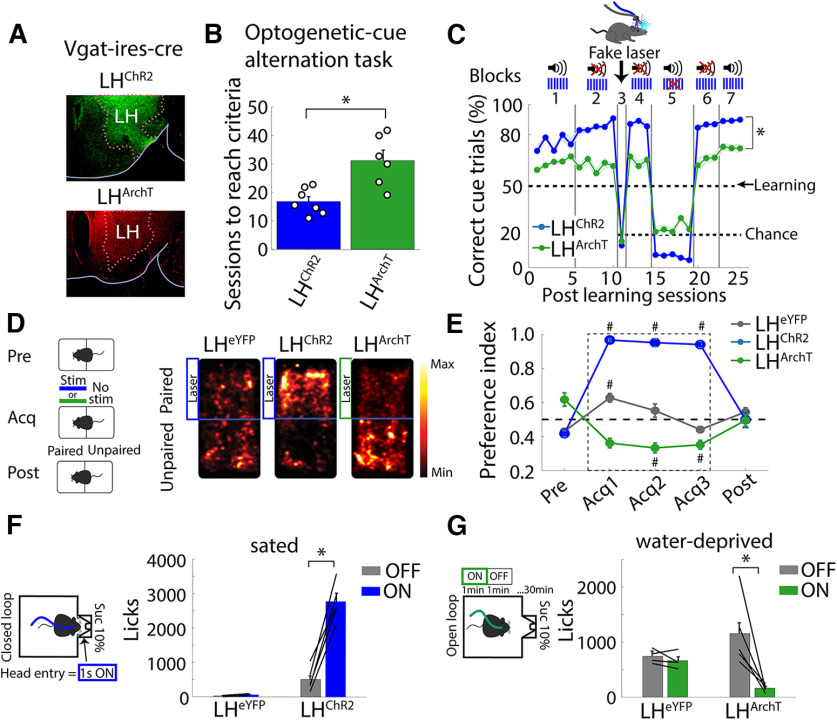
Mice could use both activation or silencing of a single cell type as a perceptible cue, although they evoked opposing behavioral effects on reward and feeding. A, Histology of mice transfected with ChR2 or ArchT in Vgat-ires-cre mice (GABAergic neurons) of the LH (LHChR2 or LHArchT, respectively). B, Sessions to reach learning criteria. Each dot represents a mouse; *p < 0.001 unpaired t tests. C, Correct trials in the presence of tone (2 kHz) and/or laser. Same conventions as in Figure 2E; *p < 0.001 two-way ANOVA (transgenic mice × block). D, Real-time Conditioned Place Preference (rtCPP). Left, rtCPP task consisted of three phases: pre-test (Pre, 1 session), acquisition (Acq, 3 sessions), and post-test (Post, 1 session). Right, Representative heat maps on the acquisition phase. Transfected Vgat-ires-cre mice with the enhanced yellow fluorescent protein (LHeYFP) were used as control. E, Fraction of time spent on the paired side. Stimulation in LHChR2 mice was rewarding (value > 0.5) while silencing in LHArchT was aversive (<0.5); #p < 0.0001, ANOVA Dunnett post hoc, relative to pre-test. F, Left, Schematic of the closed-loop task. Sated LHChR2 or LHeYFP mice were placed in a behavioral box with a sucrose sipper. Head entry into the port triggered optogenetic stimulation (1 s “on,” 20 Hz + 2 s time out, 473 nm). Right, total licks during the task. G, Left panel, Open-loop task. In water-deprived LHArchT or control LHeYFP mice, a continuous green laser was turned “on” in blocks of 1 min (532 nm) and 1 min with no-laser (“off”). Right, Total licks during the task; *p < 0.001 paired t test. Extended Data Figure 7-1 depicts a raster plot of sucrose licking during stimulation of LHChR2, LHArchT, and LHeYFP mice.