FIGURE 1.
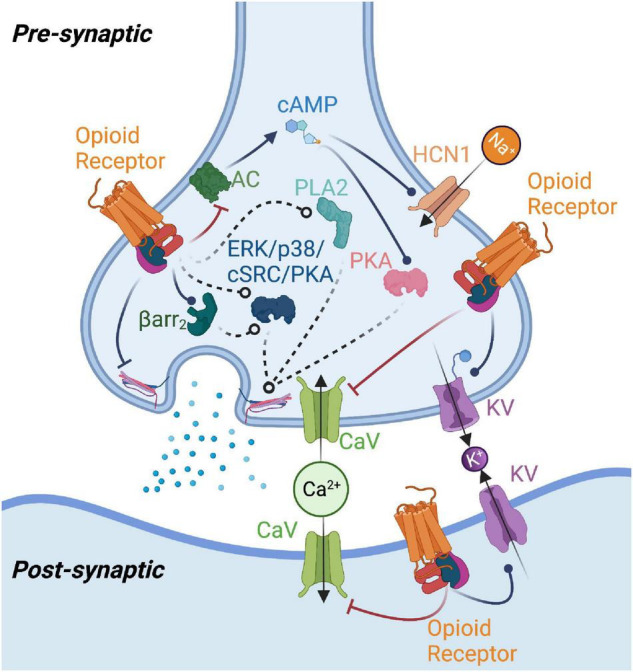
Summary of potential mechanisms of opioid receptor-mediated modulation of neurotransmission. Opioid receptor activation enhances potassium channel (KV) and inhibits calcium channel (CaV) function, reducing neurotransmitter release or producing changes in postsynaptic excitability. Opioid receptors may modulate adenylyl cyclase (AC) function to reduce cAMP levels, thereby impacting protein kinase A (PKA) and type 1 hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated (HCN1) channel activity. Beta-arrestin2 (Barr2), phospholipase A2 (PLA2), as well as kinases such as p38, ERK, protein kinase C (PKC), and cSrc have been implicated in mediating opioid receptor effects on neurotransmission. Opioid receptor-mediated G protein signaling could also directly affect neurotransmitter release machinery. Figure created with BioRender.com.
