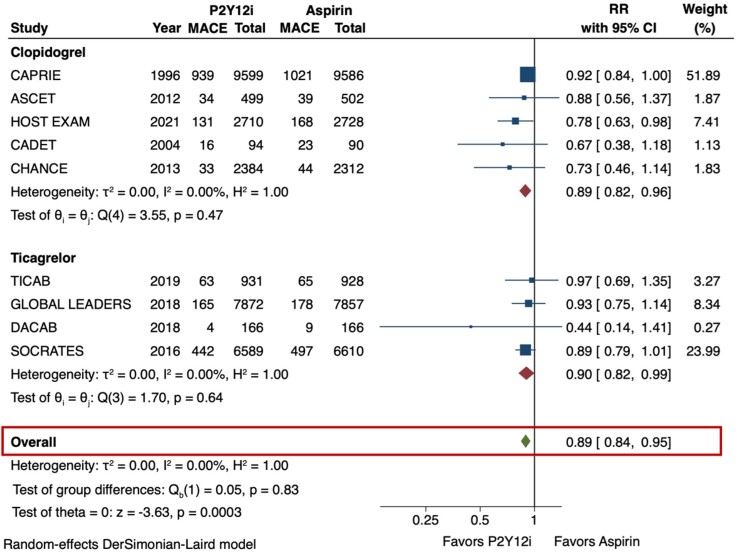
Figure 2.
Major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) in P2Y12 inhibitor monotherapy versus aspirin monotherapy. The primary efficacy outcome of interest was MACE, which was defined as a composite of stroke, myocardial infarction (MI), or death in the majority of studies. The DerSimonian and Laird random-effects model was used to examine the risk ratios (RR). All 9 trials were included for this analysis. P2Y12 inhibitor monotherapy reduced the risk of MACE by 11% as compared with aspirin monotherapy (RR 0.89 [95% CI 0.84-0.95], I2 = 0%). This result was consistent irrespective of the P2Y12 inhibitor used (p-interaction = 0.83). CI = confidence interval, MACE = major adverse cardiovascular events, P2Y12i = P2Y12 inhibitor, RR = risk ratio.