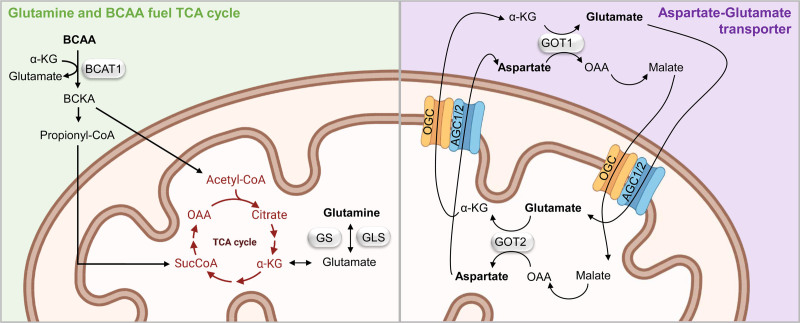
Figure 4.
Glutamine and BCAA fuel TCA cycle. Green box: glutamine and BCAA pathway. In the mitochondria, glutamine is converted in glutamate by Gls and then αKG to fuel TCA cycle. Catabolism of BCAA by BCAT1 produces cytosolic Glu. The resulting BCKA fuel the TCA cycle via acetyl-CoA or are converted into propionyl-CoA, which enters the TCA cycle producing succinyl-COa (SucCoA). Purple box: glutamate-aspartate transporter. In the cytosol, OAA is converted into malate, which is then imported into the mitochondria by OCG in exchange for αKG. In the mitochondria, malate is reconverted in OAA, which in turn is transformed into aspartate by GOT2. GOT2 also produces αKG, which is used to exchange malate from the cytosol to the mitochondria. AGC1/2 simultaneously transports glutamate from the cytosol to the mitochondrial matrix, whereas exporting aspartate from the matrix to the cytosol. In the cytosol, OAA and glutamate are regenerated by GOT1. Silver box label enzymes. Template created with BioRender.com. AGC1/2 = Aspartate/glutamate carrier 1 and 2; BCAA = branched-chain amino acid; BCAT1 = BCAA transaminase 1; BCKA = branched chain keto acids; Gls = glutaminase; Glu = glutamate; GOT2 = glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase 2; OAA = oxaloacetate; OCG = 2-oxoglutarate carrier; TCA = tricarboxylic acid; αKG = α-ketoglutarate.