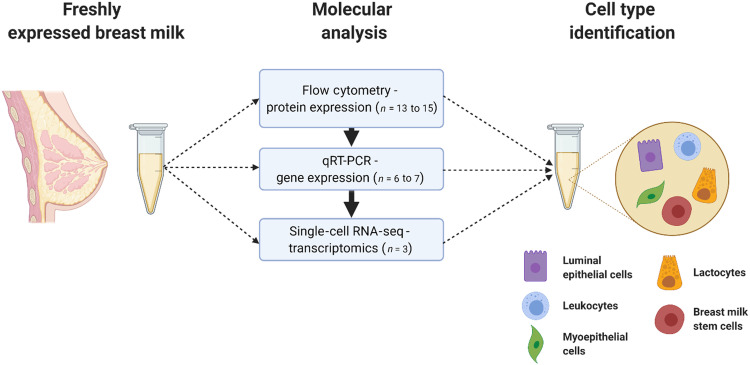
Fig. 1. Maternal cells in breast milk were identified by protein, gene, and transcriptome analyses.
Mature-stage breast milk from healthy donors was assessed for expression of cell marker proteins (e.g., EpCAM and CD45) in freshly isolated samples by flow cytometry. Then, RNA was isolated and used to conduct complementary gene expression analysis by RT-qPCR. Single-cell transcriptomics added depth to the analysis and defined the lactocyte population in breast milk.