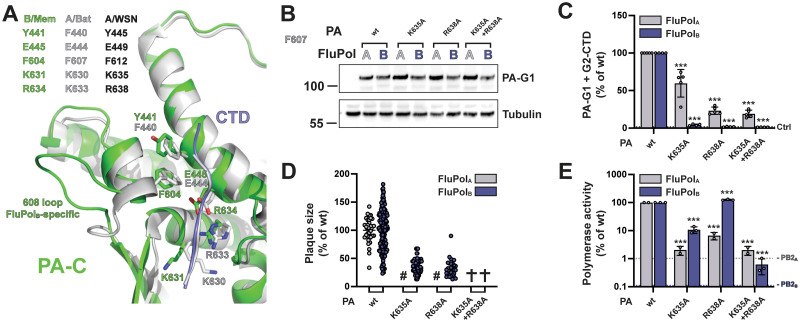
Fig 3. FluPolB and FluPolA CTD-binding mode at site 1AB.
A. Superposition of the similar CTD binding in sites 1AB on the PA subunit for influenza B (B/Memphis/13/2003, green) and bat influenza A (A/little yellow-shouldered bat/Guatemala/060/2010(H17N10), light grey) polymerases with the CTD peptide as a thin tube (respectively slate blue and light grey). Key conserved residues are indicated in their respective colours, as well as the FluPolB-specific insertion (PA 608 loop) that is important for part of site 2B. See sequence alignment in Fig 1E. B. HEK-293T cells were transfected with the indicated FluPolA (A/WSN/1933) and FluPolB (B/Memphis/13/2003) site 1AB mutants, which were C-terminally tagged with the G1 fragment. Cells were lysed at 24 hpt and analysed by western blot using antibodies specific for G.princeps luciferase (PA-G1) and tubulin. The residue numbering corresponds to FluPolA (A/WSN/1933). C. In vivo CTD binding of the indicated mutants of FluPolA (A/WSN/1933, grey bars) and FluPolB (B/Memphis/13/2003, blue bars). The G2-tagged CTD was expressed by transient transfection in HEK-293T cells together with PB2, PB1 and PA-G1. RLUs are expressed as percentages relative to wt FluPolA/B. The data shown are mean ± SD of four independent experiments performed in technical triplicates. The dotted line labelled “Ctrl” indicates the background signal i.e. the sum of the luminescence activities measured in control samples co-transfected with either the FluPol-G1 and G2 plasmids or the G1 and G2-CTD plasmids. ***p ≤ 0.001 (two-way ANOVA; Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test). D. Characterisation of recombinant IAV (A/WSN/1933, grey dots) and IBV (B/Brisbane/60/2008, blue dots) viruses. Recombinant viruses with the indicated mutations were generated by reverse genetics as described in the Materials and Methods section. Reverse genetic supernatants were titrated on MDCK cells, stained at 72 hpi and plaque diameters were determined using the Fiji software. Each dot represents the diameter of a viral plaque relative to the mean plaque size of IAV wt or IBV wt recombinant virus. (#) not measurable pinhead-sized plaque diameter; (✞) no viral rescue. E. Polymerase activity of CTD-binding site 1AB mutants. FluPolA (A/WSN/1933, grey bars) or FluPolB (B/Memphis/13/2003, blue bars) was reconstituted in HEK-293T cells by transient transfection of PB2, PB1, PA, NP and a model RNA encoding the Firefly luciferase flanked by the 5’ and 3’ non-coding regions of the IAV or IBV NS segments, respectively. As an internal control, a RNA-Polymerase II promotor driven Renilla plasmid was used. Luminescence was measured at 24 hpt as described in the Materials and Methods section. Firefly activity was normalised to Renilla activity and is shown as percentages relative to wt FluPolA/B. The data shown are the mean ± SD of three independent experiments performed in technical duplicates. The dotted lines indicate the background signals in cells transfected with FluPolA or FluPolB plasmids minus the PB2A or PB2B plasmid, respectively. ***p ≤ 0.001 (two-way ANOVA; Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test).