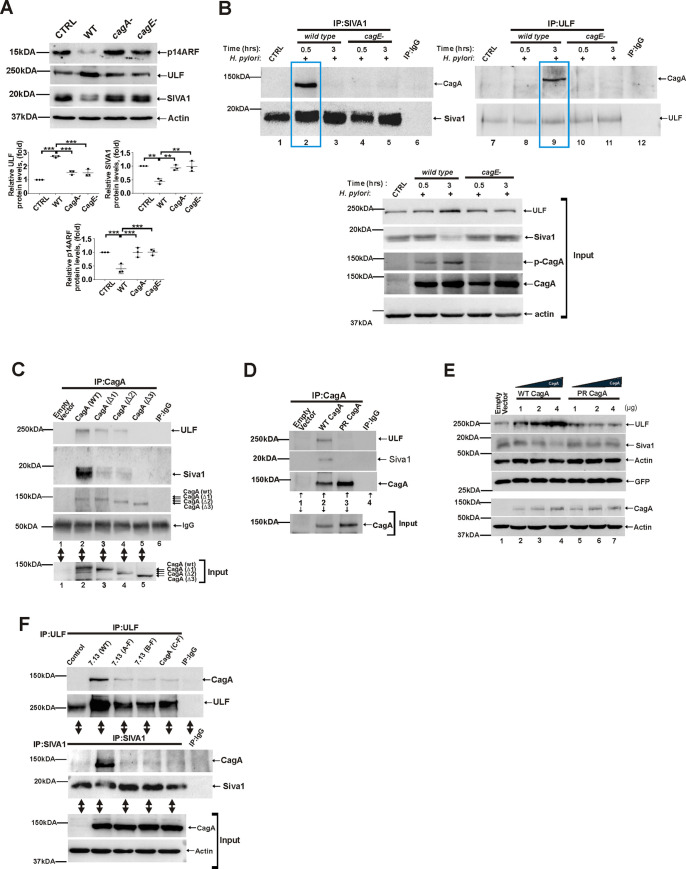
Fig 8. Bacterial CagA protein interacts with ULF and SIVA1.
(A) Expression of ULF, SIVA1 and p14ARF proteins in SNU1 cells co-cultured with H. pylori strain 7.13 or its cagA- and cagE- isogenic mutants for 6 hrs. Bottom panels show the densitometric analyses of ULF, SIVA1, and p14ARF proteins. (B) Co-immunoprecipitation analysis of CagA binding to ULF and SIVA1 proteins in SNU1 cells co-cultured with H. pylori strain 7.13 and its isogenic cagE- mutant for the indicated time periods. Equal amounts of total cell lysates were immunoprecipitated using ULF and SIVA1 antibodies and analyzed for CagA binding using anti-CagA antibody (n = 3). Immunoprecipitations with non-specific mouse and rabbit antibodies were used as controls. Two boxed areas show binding of CagA to ULF and SIVA1 proteins after their immunoprecipitation. (C) Co-immunoprecipitation analysis of CagA binding to ULF and SIVA1 proteins in AGS cells that were transfected with plasmids expressing wild type CagA or ΔEPIYA-CagA deletion mutants. Equal amounts of total cell lysates were immunoprecipitated using CagA antibody and analyzed for ULF and SIVA1 binding to CagA. Bottom panel shows input. (D) The same as (C), but AGS cells were transfected with wild type CagA expression plasmid or phosphorylation-deficient CagA mutant (PR CagA). (E) Regulation of ULF, SIVA1, and p14ARF proteins in SNU1 cells transfected with an increasing amount of wild type CagA- and PR CagA- mutant plasmids. Co-transfection with GFP-expression plasmid was used to normalize for differences in transfection efficiency. (F) Assessment of the role of the EPIYA motifs. SNU1 cells were co-cultured with wild type H. pylori strain 7.13 or its phosphorylation-deficient mutants 7. 13 (A-F), 7. 13 (B-F), or 7. 13 (C-F) and analyzed for binding of CagA to Siva1 and ULF at various time points. Interactions of SIVA1 and ULF proteins with CagA are shown at 0.5hrs and 3hrs, respectively. Bottom panel shows input. All experiments were performed three times (n = 3) with representative blots shown.