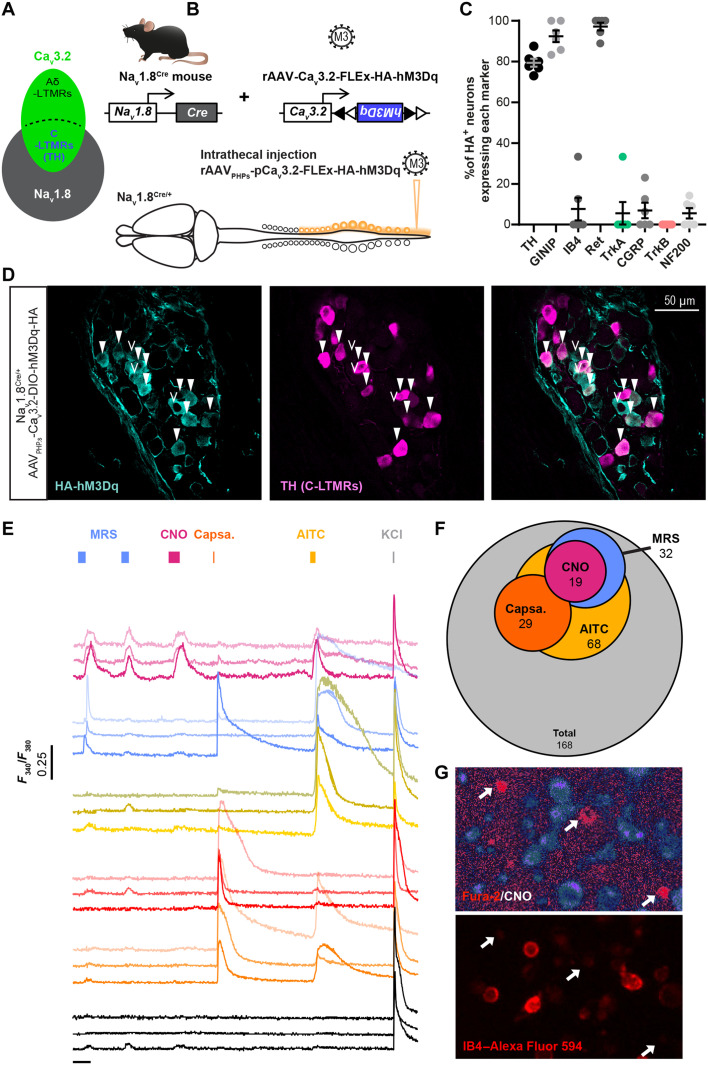
Fig. 3. Viral expression of DREADD receptors HA-hM3Dq in C-LTMRs.
(A) Diagrams representing primary sensory neurons expressing Nav1.8 and Cav3.2 and the population defined by the expression of both ion channels. (B) Strategy to express HA-hM3Dq in C-LTMRs using intrathecal injection of AAVPHPs serotypes in Nav1.8Cre mice. (C) Bar graph of the percentage of hemagglutinin (HA)–positive (HA+) neurons expressing each of the DRG population markers indicated in the x axis. Each dot represents one mouse (three sections counted per mice), n = 6 mice. (D) Representative images of an immunofluorescence of TH (C-LTMRs marker, magenta) and HA tag (HA-hM3Dq, cyan) in thoracic DRG (T13) of a Nav1.8Cre/+ mouse injected with AAVPHPs-pCav3.2-FLEx-HA-hM3Dq. Filled white arrowheads indicate examples of neurons positive for HA and TH. Empty arrowheads indicate examples of neurons positive for HA only. (E) Fura-2 representative individual calcium influx in cultured DRG neurons from Nav1.8Cre/+ mice infected with AAVPHPs-pCav3.2-FLEx-HA-hM3Dq, following bath perfusion of MRS2365 (MRS; 200 nM, blue), clozapine N-oxide (CNO) (30 μM, purple), capsaicin (Capsa., 500 nM, orange), AITC (200 μM, yellow), or KCl (40 mM, gray). (F) DRG neurons from Nav1.8Cre/+ mice infected with AAVPHPs-pCav3.2-FLEx-HA-hM3Dq responding to CNO also respond to MRS and AITC. Venn diagram for the number of neurons responding to the different chemical compounds. CNO responders (purple, n = 19), MRS responders (blue, n = 32), AITC responders (yellow, n = 68), and capsaicin responders (orange, n = 29). In total, N = 168 neurons were recorded from three animals. (G) CNO responding neurons do not bind to IB4. Representative images of ratiometric calcium imaging on cultured DRG from a Nav1.8Cre mice injected with AAVPHPs-pCav3.2-FLEx-HA-hM3Dq. Top: Ratiometric Fura-2 after CNO bath perfusion. Bottom: Live IB4–Alexa Fluor 594 staining of the same field of view. White arrows indicate CNO-responsive DRG neurons.