Figure 1. Mechanisms of pesticide-induced SNc dopamine neurodegeneration.
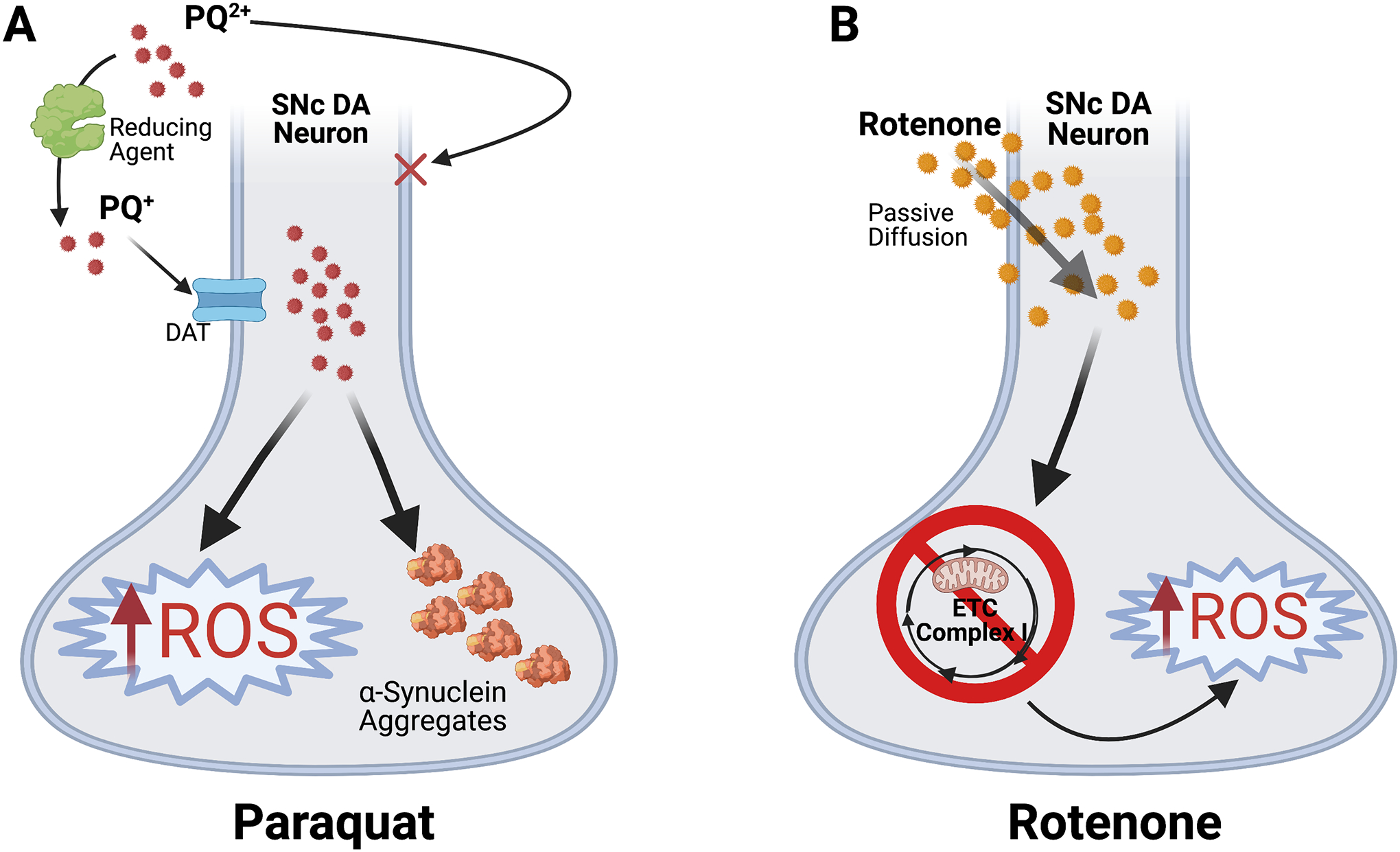
(A) Paraquat (PQ) enters the organism in its native divalent cation state, PQ2+, which cannot cross the plasma membrane. However, conversion to PQ+ by a reducing agent enables PQ+ to selectively enter DA neurons via the dopamine transporter (DAT)34. PQ+ accumulates in neurons where it induces increased ROS generation and α-synuclein aggregation35. Resulting oxidative stress contributes to SNc DA neurodegeneration. (B) Rotenone is lipophilic and freely crosses the membrane via passive diffusion36. Rotenone then induces ROS buildup and neurotoxic oxidative stress via direct inhibition of Complex I of the mitochondrial electron transport chain (ETC)25.
